Generic JDBC Select
Overview
You can use this Snap to fetch data from the connected database by providing a table name and configuring the connection. This Snap also supports DML operation (SELECT) when using the AWS Athena database. This Snap produces the records from the database on its output, view which can then be processed by a downstream Snap.
SELECT * FROM [table] WHERE [where clause] ORDER BY [ordering] LIMIT [limit] OFFSET [offset]A good example for a where clause is: SALARY = $SALARY (here, we use the SALARY variable of the input document).
Read-type Snap
Works in Ultra Tasks
Known issues
- The metadata output in the second output preview is not displayed in a table format when your target database is AWS Athena.
-
The suggestions list is not populated for the Table name field when your target database is AWS Athena.
-
When the Generic JDBC - Select Snap connects to the Sybase database to retrieve
BigTime-type data, the Snap displays both date and time for the data type.
Snap views
| View | Description | Examples of upstream and downstream Snaps |
|---|---|---|
| Input |
Document that provides values for one or more properties of the Snap or simply for pass through purposes. This Snap has at most one document input view. If the input view is defined, then the where clause can substitute incoming values for a given expression, such as a table name or as a variable as part of the WHERE clause. |
|
| Output |
Document for each record retrieved. Special types such as TIMESTAMP, TIMESTAMPTZ and TIMESTAMPLTZ are converted into SnapLogic internal date type representations which then can be consumed by downstream Snaps just like any other data type. This Snap has one document output view by default A second view can be added to dump out the metadata for the table as a document. The metadata document can then be fed into the second input view of a database Insert or Bulk Load Snap so that the table is created in the database with a similar schema as the source table. |
|
| Error |
Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter when running the pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab. The available options are:
Learn more about Error handling in Pipelines. |
|
Snap settings
- Expression icon (
): Allows using pipeline parameters to set field values dynamically (if enabled). SnapLogic Expressions are not supported. If disabled, you can provide a static value.
- SnapGPT (
): Generates SnapLogic Expressions based on natural language using SnapGPT. Learn more.
- Suggestion icon (
): Populates a list of values dynamically based on your Snap configuration. You can select only one attribute at a time using the icon. Type into the field if it supports a comma-separated list of values.
- Upload
 : Uploads files. Learn more.
: Uploads files. Learn more.
| Field / Field set | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
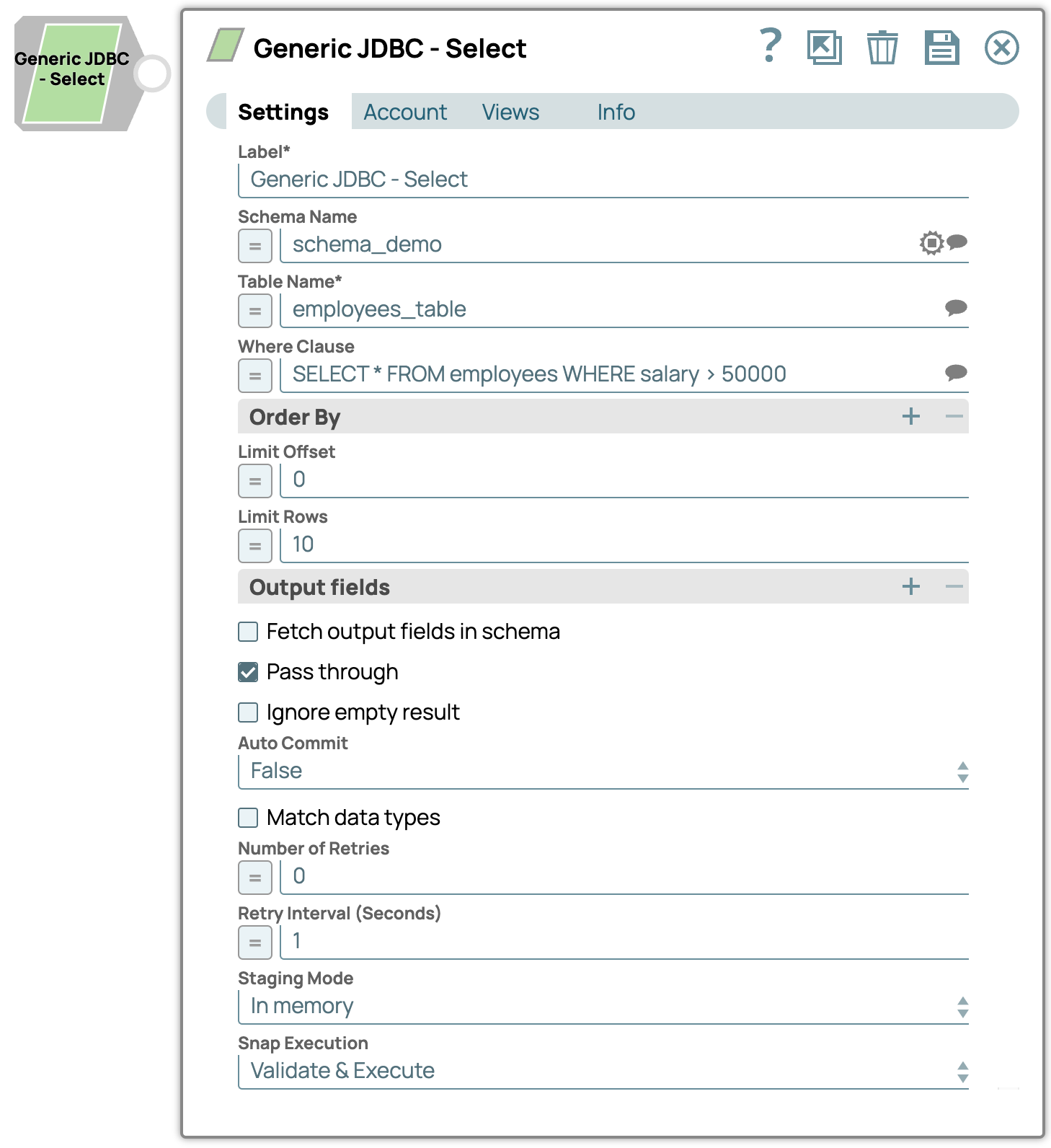
| Label | String | Required. Specify a unique name for the Snap. Modify this to be more appropriate, especially if more than one of the same Snaps is in the pipeline. Default value: Generic JDBC - Select Example: Generic JDBC - Select |
| Schema Name | String/Expression/ Suggestion | The database schema name. Selecting a schema filters the Table name list
to show only those tables within the selected schema. Default value: N/A Example: schema_demo |
| Table Name | String/Expression/ Suggestion | Required. Specify the table to execute the select query
on. Default value: N/A Example: employees_table |
| Where Clause | String/Expression/ Suggestion |
Specify the WHERE clause of the SELECT statement. This supports document value substitution (such as $person.firstname will be substituted with the value found in the incoming document at the path). However, you may not use a value substitution after "IS" or "is" word. Examples: Without using expressions
Using expressions
Warning: Using expressions that join strings together to create SQL
queries or conditions has a potential SQL injection risk and is hence unsafe.
Ensure that you understand all implications and risks involved before using
concatenation of strings with '=' Expression enabled.
Default value: N/A Example: SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary > 50000 |
| Order By | Use this fieldset to specify the columns in the order in which you want to sort the database. The default database sort order will be used. | |
| Column Names | String/Expression |
Specify the column names. Default value: N/A Example: name |
| Limit offset | Integer/Expression | Specify the offset for the limit clause. This is where the result set should
start. Starting row for the query. Note that some databases do not support OFFSET,
such as Teradata, and the Limit offset property is ignored. Default value: N/A Example: 0 |
| Limit rows | Integer/Expression | Specify the number of rows to return from the query. Default value: N/A Example: 10 |
| Output fields | Use this fieldset to specify the output fields for SQL SELECT statement. | |
| Output field | String/Expression | Specify or select output field names for SQL SELECT statement. To select all
fields, leave it at default. Default value: N/A Example: email, address, first, last |
| Fetch Output Fields In Schema | Checkbox | Select this check box to include only the selected fields or columns in the
Output Schema (second output view). If you do not provide any Output fields,
all the columns are visible in the output. If you provide output fields, we recommend you to select Fetch Output Fields In Schema check box. Default status: Deselected |
| Pass-through | Checkbox | Select to make the input document will be pass through the output view under
the key 'original'. Default status: Selected |
| Ignore empty result | Checkbox | Select if you want no document to be written to the output view when a SELECT
operation does not produce any result. If this property is not selected and the
Pass-through property is selected, the input document will be passed
through to the output view. Default status: Deselected |
| Auto Commit | Dropdown list | Select one of the options for this property to override the state of the
Auto commit property on the account. The Auto commit at the
Snap-level has three values: True, False, and Use account
setting. The expected functionality for these modes are:
Default value: False Example: True |
| Match data types | Checkbox |
This property applies only when the Output fields property is provided with any field value(s). If this property is selected, the Snap tries to match the output data types same as when the Output fields property is empty (SELECT * FROM ...). The output preview would be in the same format as the one when SELECT * FROM is implied and all the contents of the table are displayed. Default status: Deselected |
| Number of Retries | Integer/Expression | Specify the maximum number of attempts to be made to receive a response. The
request is terminated if the attempts do not result in a response. Note: If the
value is larger than 0, the Snap first downloads the target file into a temporary
local file. If any error occurs during the download, the Snap waits for the time
specified in the Retry interval and attempts to download the file again from the
beginning. When the download is successful, the Snap streams the data from the
temporary file to the downstream Pipeline. All temporary local files are deleted
when they are no longer needed. Default value: 0 Example: 3 |
| Retry Interval (seconds) | Integer/Expression |
Specify the time interval between two successive retry requests. A retry happens only when the previous attempt resulted in an exception. Default value: 1 Example: 10 |
| Staging mode | Dropdown list | Required when the value in the Number of retries field is greater
than 0.
Specify the location from the following options to store input documents between retries:
Default value: In memory Example: On disk |
| Snap execution | Dropdown list |
Choose one of the three modes in
which the Snap executes. Available options are:
Default value: Execute only Example: Validate & Execute |
-
For the 'Suggest' in the Order by columns and the Output fields properties, the value of the Table name property should be an actual table name instead of an expression. If it is an expression, it will display an error message "Could not evaluate accessor: ..." when the 'Suggest' button is clicked. This is because, at the time the "Suggest" button is clicked, the input document is not available for the Snap to evaluate the expression in the Table name property. The input document is available to the Snap only during the preview or execution time.
-
Teradata does not support LIMIT OFFSET clause. If Teradata is connected to the Generic JDBC - Select Snap, it uses the Limit rows value in the TOP n operator and ignores the Limit offset value.


