Ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- A user or service account with read and execute access to the project containing the Triggered Task.
- The URL for the Triggered Task, including any Pipeline parameters and their values.
- Read and execute permissions on the node(s) running the Triggered Task.
- For use on Windows servers, a Cygwin shell with curl.
Enterprise job schedulers that execute long-running Triggered Task Pipelines can
experience timeout or lost client connection errors. To mitigate these issues, use the
snaplogic_exec.sh script. This script can be executed on any server
with network access to the Triggered Task URL, maintaining the connection and preventing
errors even for long-running tasks. Attention: The SnapLogic_exec.sh script
was developed for a specific use case and is not part of our officially maintained
or certified artifacts. The script will not be regularly updated or
tested.
-
Install the script on a server accessible by the Scheduler and configure it with your SnapLogic credentials.
-
Download snaplogic_exec.zip.
-
Extract the compressed file and save the
snaplogic_exec.sh script to the appropriate location. For example, use /usr/local/bin on Linux or %systemroot%\System32\Repl\Imports\Scripts on Windows.
-
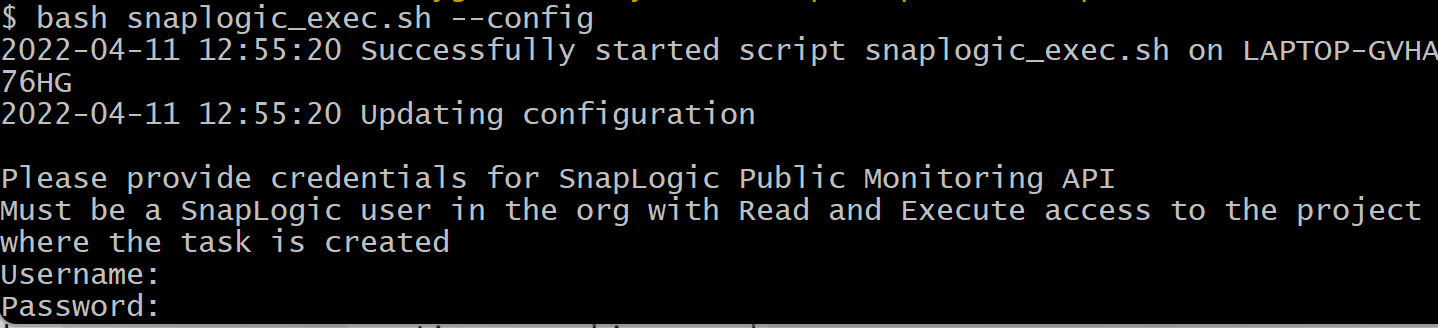
From the directory containing the script, run
snaplogic_exec.sh --config in a terminal window. For example, on Windows:
-
Enter the SnapLogic username and password when prompted.
-
Configure the pipeline to work with the script:
-
Open the pipeline in SnapLogic Designer.
-
Add a Mapper Snap to the canvas.
-
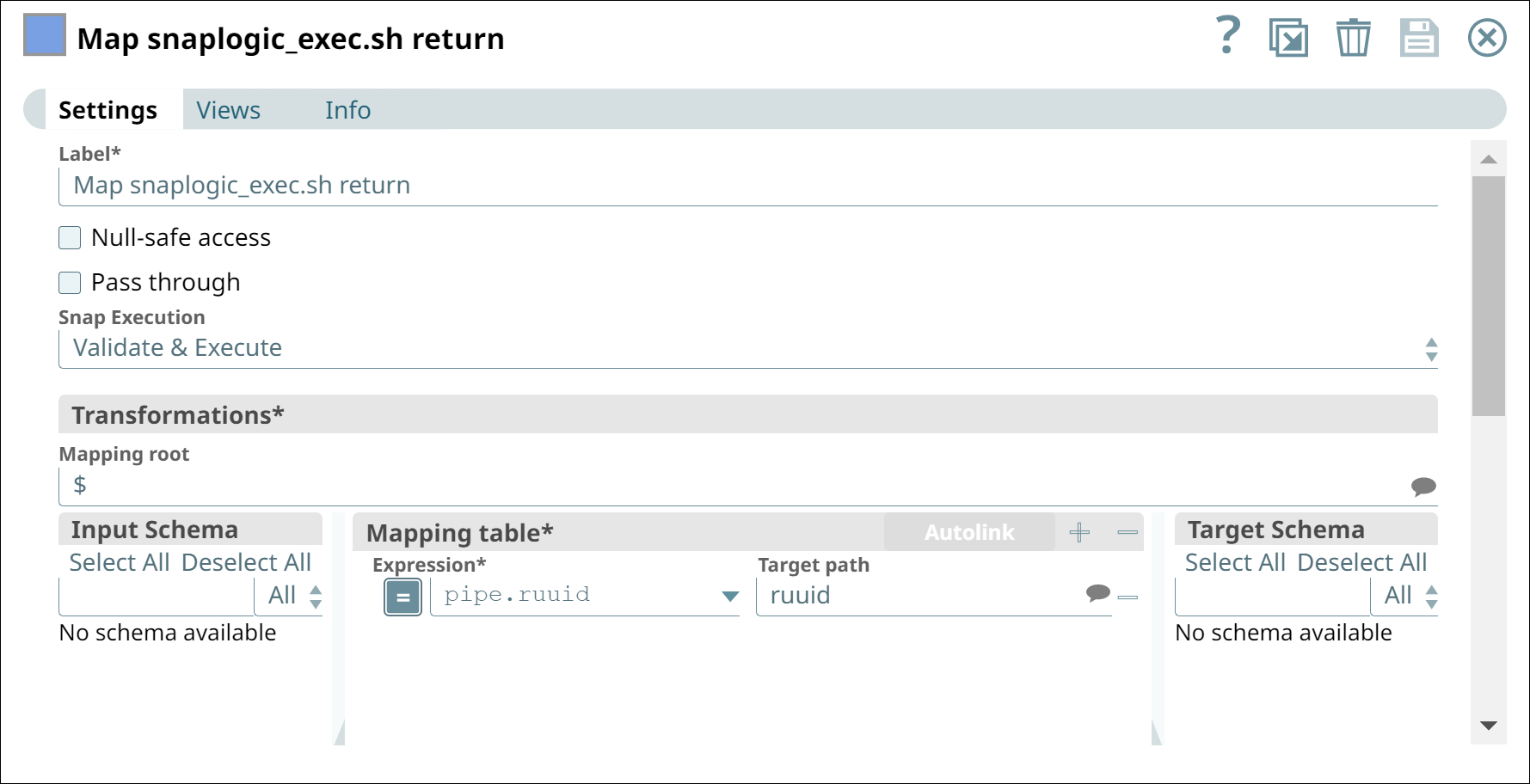
In the Settings tab, enter Map snaplogic_exec.sh return in the Label field.
-
In the Mapping table, add the Expression
pipe.ruuid with the Target path
ruuid.
-
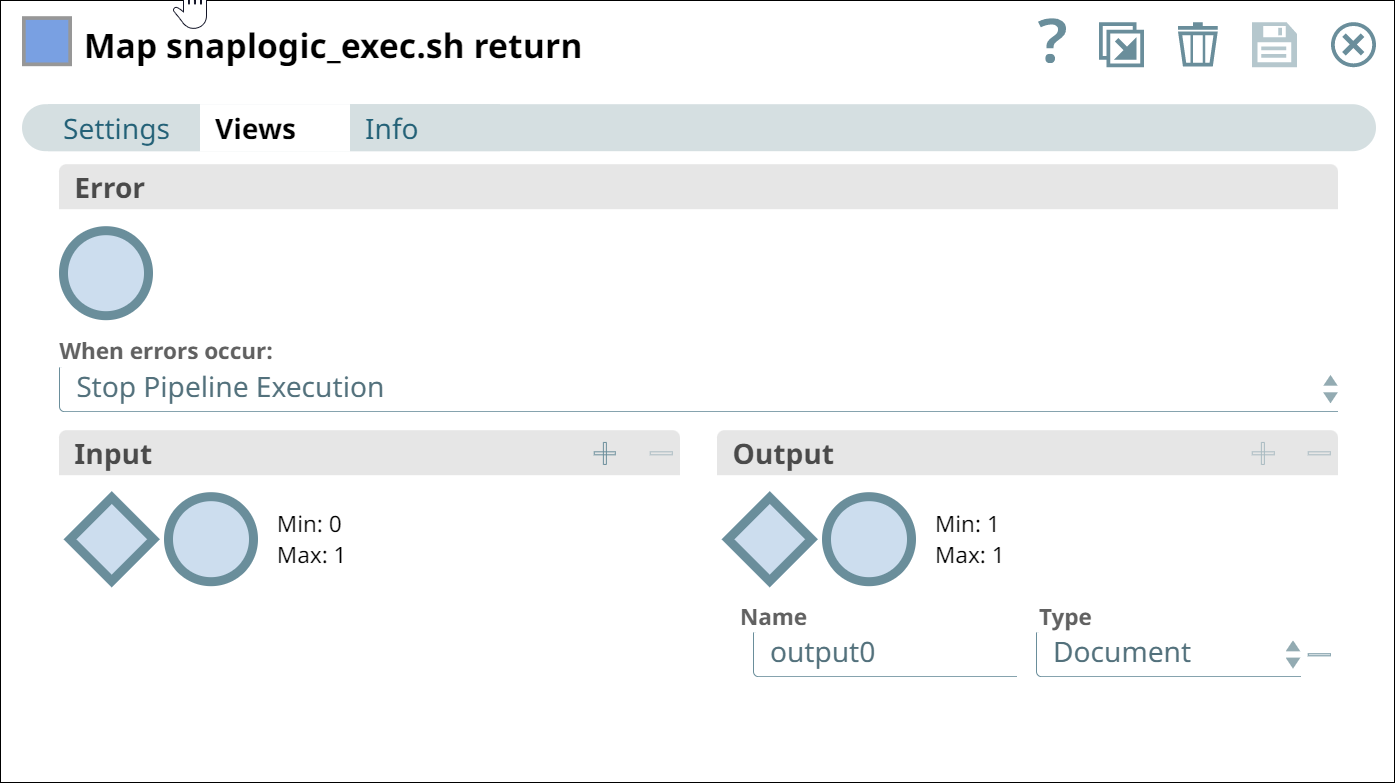
Select the Views tab and click the minus (-) icon to remove the input view.
-
Leave the default output view,
output0, as is, with Type document.
-
Save and close the Mapper Snap.
-
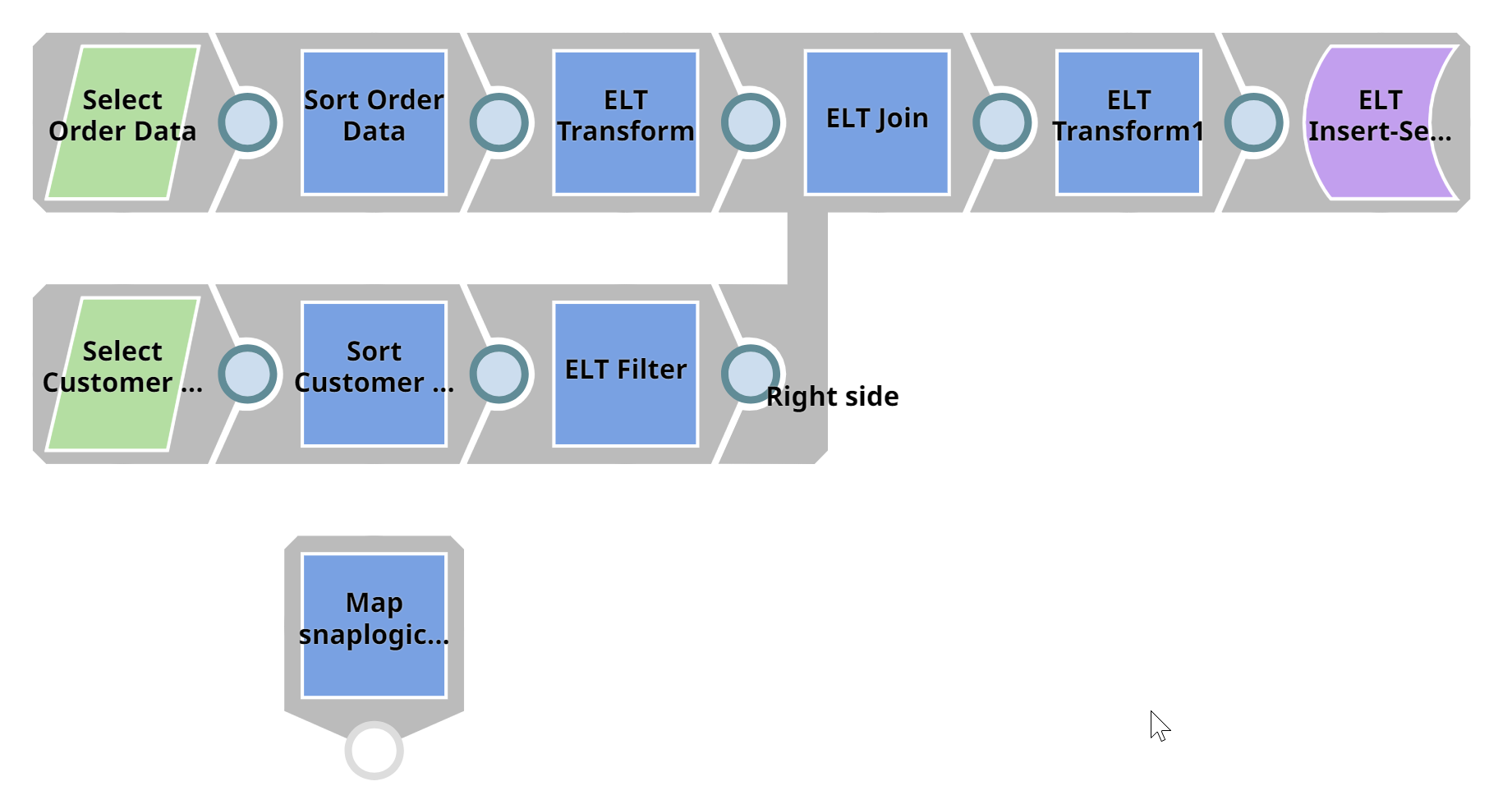
The pipeline should look similar to the following (before validation):
-
Run the script from the scheduler
The invocation must include your Org name and the Triggered Task URL. For example:
snaplogic_exec.sh --org <my_org>
"https://elastic.snaplogic.com/api/1/rest/slsched/feed/<task_path>?param1=<param-value>?param2=<param2-value>"
The following table lists snaplogic_exec.sh command options.
| Command |
Shortcut |
Description |
--config |
-c |
Creates or updates a snaplogic_exec.credentials file to store the credentials used by the Public Monitoring API. Run this command before invoking it to run the Triggered Task. |
--org |
-o |
Specifies the SnapLogic Org containing the pipeline to execute. (Required) |
--seconds |
-s |
Specifies the number of seconds between Public Monitoring API calls. (Default 30) |
--retry |
-r |
Specifies the maximum number of times to retry the Public Monitoring API call before terminating the script |
--verbose |
-v |
Enables more messages during script execution |
--debug |
-d |
Enables debug messages during script execution |
-help or -usage |
|
Outputs parameters and command options to the terminal window |
Using the snaplogic_exec.sh should enable you to execute long-running Triggered Tasks from an enterprise scheduler without causing timeout or lost connection errors.
If you encounter issues with the script, run it using the --debug and --verbose commands. They display messages as commands execute, and report all responses.