Profile
Overview
You can use this Snap to compute statistics on the incoming data and derive a statistical analysis of the data in data sets. Each field can be either numerical or categorical. You can use the Type Converter Snap to appropriately change the data type.
Transform-type Snap
Does not support Ultra Tasks
Prerequisites
- The input document cannot have a nested structure.
Limitations and known issues
None.
Snap views
| View | Description | Examples of upstream and downstream Snaps |
|---|---|---|
| Input | This Snap supports a maximum of one document input view. It requires the data set as an input. |
|
| Output | This Snap supports a maximum of two document output views. Statistical details
of the data set. Computation is different based on the type of fields.
Second Output view: When enabled, this view outputs an HTML file that is a graphical visualization of the first output. If you select the Value distribution property, the value distribution of each class is also included in the output. Select this checkbox to view the statistics in a graph and produce an HTML file that displays a graph of the first output. |
Mapper |
| Error |
Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter when running the pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab. The available options are:
Learn more about Error handling in Pipelines. |
|
Snap settings
- Expression icon (
): Allows using JavaScript syntax to access SnapLogic Expressions to set field values dynamically (if enabled). If disabled, you can provide a static value. Learn more.
- SnapGPT (
): Generates SnapLogic Expressions based on natural language using SnapGPT. Learn more.
- Suggestion icon (
): Populates a list of values dynamically based on your Snap configuration. You can select only one attribute at a time using the icon. Type into the field if it supports a comma-separated list of values.
- Upload
 : Uploads files. Learn more.
: Uploads files. Learn more.
| Field / Field set | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Label | String |
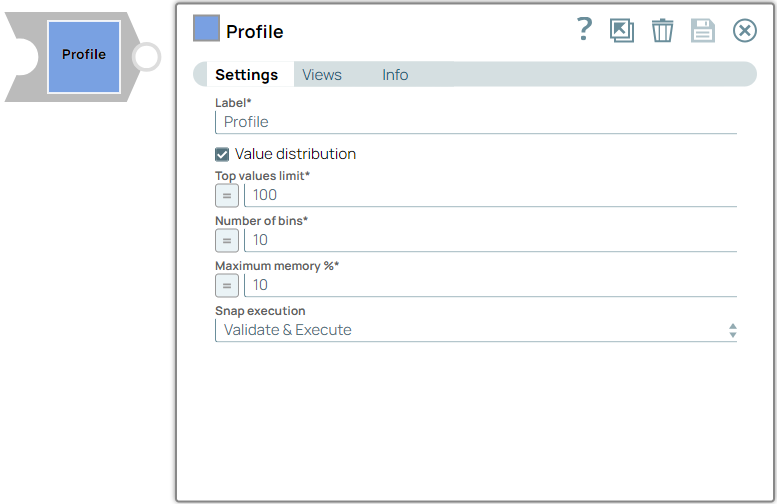
Required. Specify a unique name for the Snap. Modify this to be more appropriate, especially if more than one of the same Snaps is in the pipeline. Default value: Profile Example: Customer data |
| Value distribution | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to include the value distribution of the fields in the output. Default status: Selected |
| Top values limit | Integer/Expression | Required. Specify the limit of the number of
value-frequency pairs in the value distribution.
Note:
Default value: 100 Example: 200 |
| Number of bins | Integer/Expression | Required. Specify the number of bins. Binning is a method
of splitting the data space into equally sized ranges where N is the number of
bins. Note:
Default value: 10 Example: 20 |
| Maximum memory % | Integer/Expression | Required. Specify the maximum percentage of the node's
memory that is used to buffer the incoming data set. Note:
Default value: 10 Example: 20 |
| Snap execution | Dropdown list |
Choose one of the three modes in
which the Snap executes. Available options are:
Default value: Validate & Execute Example: Execute only |
Temporary files
During execution, data processing on Snaplex nodes occurs principally in-memory as streaming and is unencrypted. When processing larger datasets that exceed the available compute memory, the Snap writes unencrypted pipeline data to local storage to optimize the performance. These temporary files are deleted when the pipeline execution completes. You can configure the temporary data's location in the Global properties table of the Snaplex node properties, which can also help avoid pipeline errors because of the unavailability of space. Learn more about Temporary Folder in Configuration Options.


