Clustering
Overview
Clustering groups similar objects together, ensuring items within a group are more alike than those in other groups. Clustering is a type of unsupervised learning. Unsupervised learning is a technique in which you can draw inferences from datasets consisting of data without labeled responses.
You can use this Snap determine the intrinsic grouping among unlabeled numeric data. If your data has categorical fields, the Snap ignores all such fields.
Transform-type Snap
Does not support Ultra Tasks
Prerequisites
None.
Limitations and known issues
None.
Snap views
| View | Description | Examples of upstream and downstream Snaps |
|---|---|---|
| Input |
Accepts one input view that provides the dataset for clustering:
|
|
| Output |
Produces one output view containing the clustering results:
|
|
| Error |
Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter when running the pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab. The available options are:
Learn more about Error handling in Pipelines. |
|
Snap settings
- Expression icon (
): Allows using JavaScript syntax to access SnapLogic Expressions to set field values dynamically (if enabled). If disabled, you can provide a static value. Learn more.
- SnapGPT (
): Generates SnapLogic Expressions based on natural language using SnapGPT. Learn more.
- Suggestion icon (
): Populates a list of values dynamically based on your Snap configuration. You can select only one attribute at a time using the icon. Type into the field if it supports a comma-separated list of values.
- Upload
 : Uploads files. Learn more.
: Uploads files. Learn more.
| Field / Field set | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
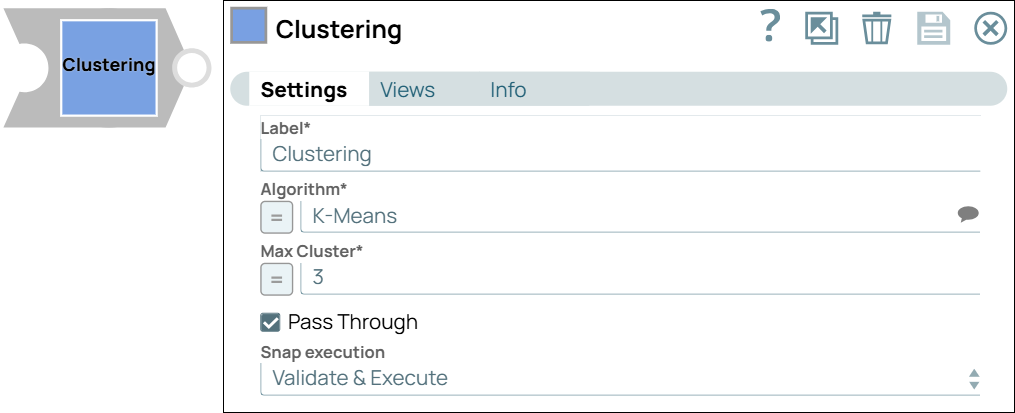
| Label | String | Required. Specify a unique name for the Snap. Modify this to be more appropriate, especially if more than one of the same Snaps is in the pipeline. Default value: Clustering Example: Cluster data |
| Algorithm | String/Suggestion |
The clustering algorithm used to group data into specific clusters. The available options are:
Default value: K-Means Example: X-Means |
| Max Cluster | Integer/Expression |
Enter the maximum number of clusters that the Snap must create. Default value: 3 Example: 5 |
| Pass Through | Checkbox |
Includes the original dataset in the output along with the cluster assignments. Default status: Selected |
| Snap execution | Dropdown list | Choose one of the three modes in which the Snap executes. Available options
are:
|


