Endpoint configuration
Endpoint configuration differs for native and external endpoints. Native endpoints call Triggered or Ultra Tasks that run on the specified Snaplex. The Snaplex that receives the request executes the task and returns the response. In contrast, for external endpoints, the Snaplex that receives the request forwards that request to a third-party or another Snaplex. Refer to Request execution flow for more information.
Native endpoints
For a native endpoint, you can select a Triggered or an Ultra task for which you have execute permission. Refer to Assign project permissions for information on permissions.
An endpoint must have at least one path and at least one HTTP method. Optionally, you can add advanced routing rules that must return true to execute the endpoint. Advanced routing rules can be an expression or a set of rules.
The following shows the New endpoint panel. The fields are the same for a Triggered or an Ultra Task:
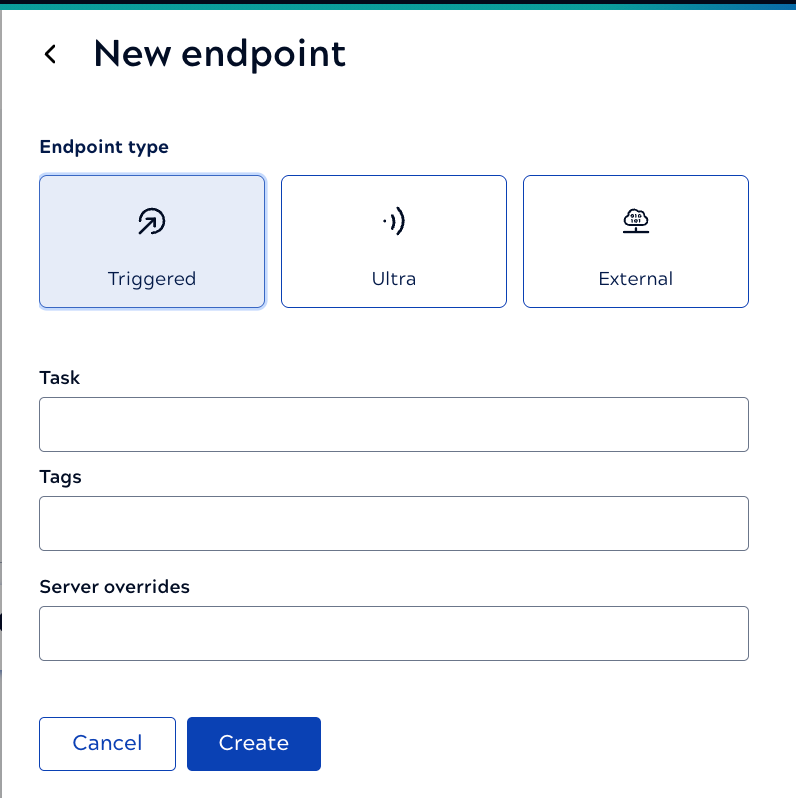
Endpoint configuration includes:
- A reference to a Triggered Task, Ultra Task
- Tags that group related endpoints together in the development environment and on the Service card when published in the APIM 3.0 Developer Portal. You can override tags at the method level. Without a tag, an endpoint shows up as ungrouped.
- Optionally, one or more Server overrides. Without a Server override, the Server selected for the Service handles the request.
External endpoints
The following shows the fields available for external endpoints:

An external endpoint includes these properties:
- The upstream URL.
- Tags that group related endpoints together in the development environment and on the Service card when published in the APIM 3.0 Developer Portal. You can override tags at the method level. Without a tag, an endpoint shows up as ungrouped.
- Optionally, one or more Server overrides. Without a Server override, the Server selected for the Service handles the request.
- Options:
- Trust all certificates: The receiving Snaplex trusts all certificates supplied by the server for the external endpoint.
- REST to SOAP: Exposes SOAP endpoints to clients through REST and translates SOAP responses to JSON. Refer to Wrap legacy SOAP APIs in a Service for more information
Snaplex selection
When you select different Snaplexes at the Service level and endpoint level, API Management 3.0 uses the Snaplex associated with the endpoint. Ultra Tasks should run on the Snaplex configured in the task. For Triggered Tasks, you can select a single or multiple Snaplexes.
Endpoint Paths
An endpoint path routes requests. When you create an endpoint, you must define one or more paths for it. Services created from specifications automatically include the endpoint paths. To learn more about the purpose and functionality of the path and method definitions, refer to the OpenAPI Specification.
Each endpoint path includes:
- The path value.
- Optional rules or expressions for advanced routing.
- An optional upstream URL.
- The supported HTTP methods.
- For each method:
- For PUT, PATCH, and POST methods, a request schema and optional example.
- Response codes and descriptions.
- Optional response body, schema, and example.
Advanced routing example
Advanced routing determines which endpoint to invoke based on rules or expressions. A rule is a name-value pair for a query parameter, header, or path parameter.
For example, a calculator Service might have two endpoints, one that accepts JSON input and one that accepts XML input. You can use the same path name for both and have APIM 3.0 route requests based on a value, such as the content-type in the header. The rule or expression that you supply must evaluate to true for the request to be routed to that path.
The following image shows two paths, one for the JSON route and one for the XML route. The rule
evaluates the header value for Content-type to determine which path to route the
request to.

Related content
The following describe how to perform tasks related to endpoints:


