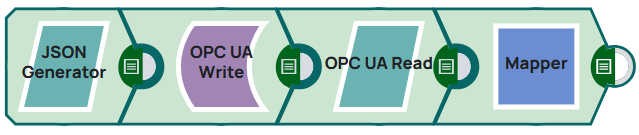
This example pipeline demonstrates handling of different data types in
OPC UA communications, covering the most common data types used in industrial automation and
control systems. It starts by generating JSON data with node IDs and values, writes these
values to specified OPC UA nodes, reads back the values from the same nodes, and maps the
results.
-
Configure the JSON
Generator Snap with the
following data containing node IDs and values of different data types (Integer, Boolean,
Byte, DateTime, and Double).
[{
"nodeId": "ns=3;i=1007",
"value": 2
},
{
"nodeId": "ns=5;s=BooleanDataItem",
"value": false
},
{
"nodeId": "ns=5;s=ByteDataItem",
"value": 1
},
{
"nodeId": "ns=5;s=DateTimeDataItem",
"value": "2024-05-15T10:30:00+05:30"
},
{
"nodeId": "ns=5;s=DoubleDataItem",
"value": 1.2
}
]
Each object in this array represents a node in an OPC UA server.
-
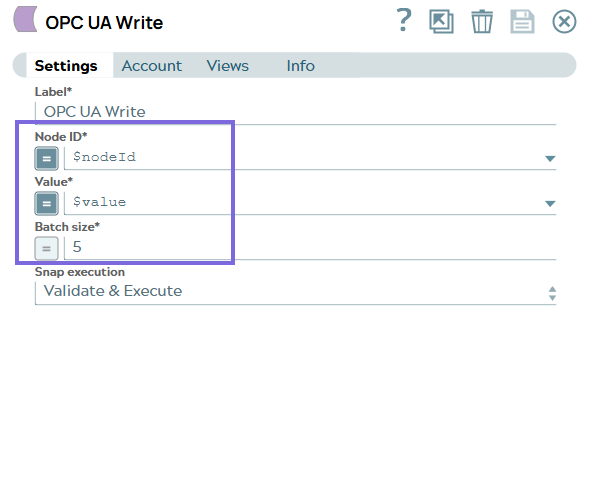
Configure the OPC UA Write Snap to write values
to specified OPC UA nodes using the Node ID and Value from the upstream JSON input.
On validation, the Snap writes the following output, which indictes that the values
were successfully written to the specified nodes in the OPC UA server. In OPC UA, a status
code of 0 (Good) is the best possible outcome, indicating that the operation completed
without any issues or warnings.
-
Configure the OPC UA Read Snap to read values
from the specified OPC UA nodes using the Node ID.
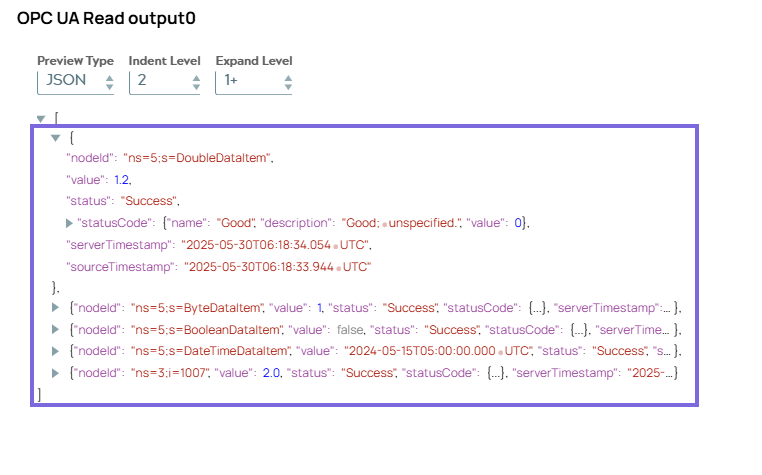
On validation, the Snap reads data from all nodes and displays the following output.
The successful status codes across all readings indicate that the OPC UA Read operation
completed without any issues for all nodes.
-
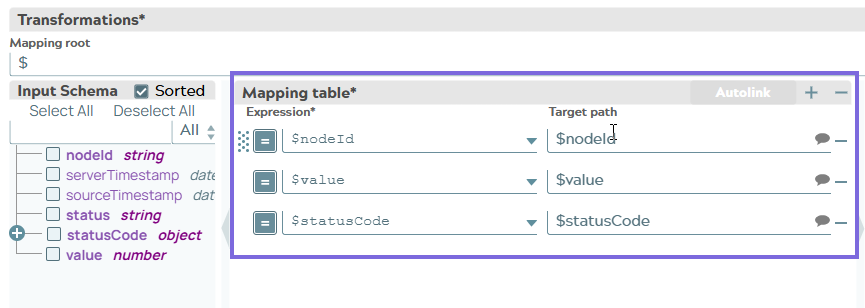
Configure the Mapper Snap to map the final
output (Node ID, Value, and Status code fields) for downstream use.
To successfully reuse pipelines:
- Download and import the pipeline in to the SnapLogic Platform.
- Configure Snap accounts, as applicable.
- Provide pipeline parameters, as applicable.