REST Get [Not Recommended]
Overview
Read-type Snap
Works in Ultra Tasks
Limitations
The REST GET Snap Link HTTP response header maybe be malformed compared to other third-party applications like POSTMAN.
Snap views
| View | Description | Examples of upstream and downstream Snaps |
|---|---|---|
| Input | Each input document offers details associated with the data required from the target RESTful server. | |
| Output | Each output document contains data retrieved from the RESTful web
server. If the Snap fails during the operation, it sends an error document to the error view containing the fields error, reason, resolution, and stacktrace. However, you must enable the Error view to view the error document. |
|
| Error |
Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter when running the pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab. The available options are:
Learn more about Error handling in Pipelines. |
|
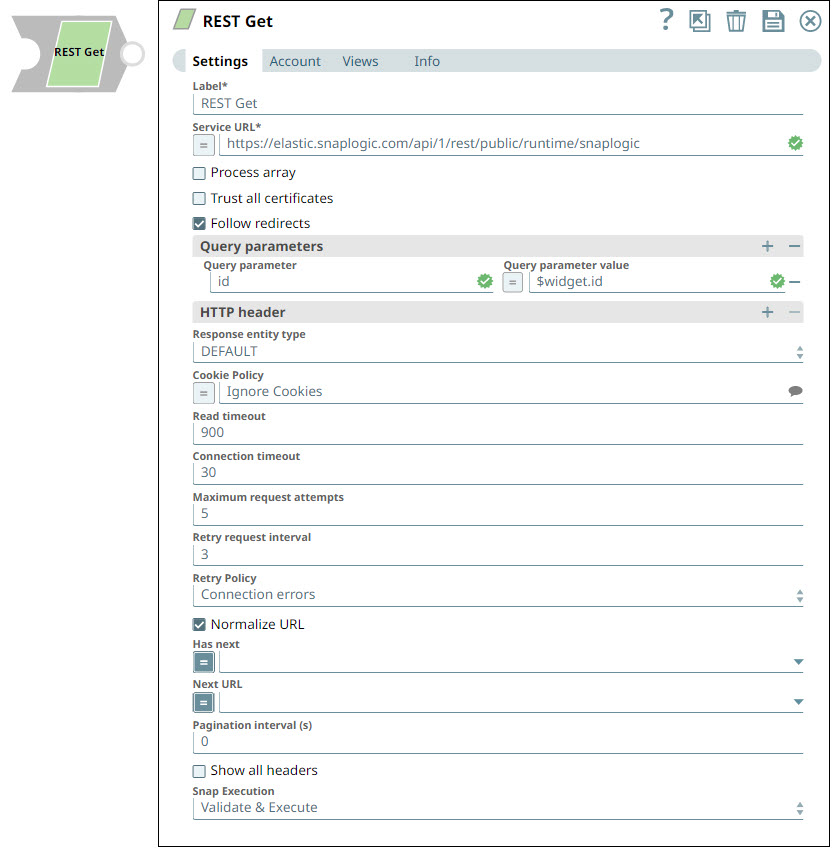
Snap settings
- Expression icon (
): Allows using JavaScript syntax to access SnapLogic Expressions to set field values dynamically (if enabled). If disabled, you can provide a static value. Learn more.
- SnapGPT (
): Generates SnapLogic Expressions based on natural language using SnapGPT. Learn more.
- Suggestion icon (
): Populates a list of values dynamically based on your Snap configuration. You can select only one attribute at a time using the icon. Type into the field if it supports a comma-separated list of values.
- Upload
 : Uploads files. Learn more.
: Uploads files. Learn more.
| Field / Field set | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Label | String | Specify a name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially
if you have more than one of the same Snap in your pipeline. Default value: REST Get Example: Get User Details |
| Service URL | String/Expression |
Required. Specify the service endpoint URL of REST API. You can provide the URL in one of the following ways:
For Snaps using AWS Signature V4 accounts, you can use the canonical name (CNAME) for the URI so it's not necessary for the URL to end with amazonaws.com or have the region and service provided in it. However, if you are using the CNAME you must provide it in the AWS Region and Service Name fields in the AWS Signature V4 account. The host name in the CNAME must be equal to the bucket name. For example:
Here, the bucket name is
The Snap finds the value at the JSON path $.widget.id in the input data and replaces "%s" in the Service URL with the value. You can connect File Reader and JSON Parser Snaps upstream of a REST Put Snap and prepare the following JSON file for the File Reader Snap: Note:
The Service URL for a REST snap must be valid. If the Service URL contains any special characters, such as !, =, %21, $, and ^, the Snap throws an exception error. You can escape the special characters (using expression language) with one of the following methods:
We recommend that you use the encodeURIComponent method to escape the special characters. Default value: N/A Example: https://elastic.snaplogic.com/api/1/rest/public/runtime/snaplogic?start=1430377200000&end=1430420399000 |
| Process array | Checkbox |
Select to produce a stream of documents with one record in each document.
Default value: Deselected |
| Trust all certificates | Checkbox |
Select this checkbox to trust all certificates, such as self-signed certificates. Default value: Deselected |
| Follow redirects | Checkbox |
Select this checkbox to enable the Snap to follow redirects.
Default value: Selected |
| Query parameters |
Use this field set to add query parameters to your request. This field set comprises the following fields:
|
|
| Query parameter | String | The name of the query parameter. Default value: N/A Example: id |
| Query parameter value | String/Expression | The value that you want to assign to the parameter. Note: This property is
expression-enabled. For more information on the expression
language, see Understanding Expressions in SnapLogic and Using Expressions. For
information on pipeline parameters, see Pipeline Properties.
Default value: N/A Example: $widget.id |
| HTTP Header |
Use this field set to create the HTTP header key-value pairs required for defining the headers for different types of input (JSON, PDF, DOCX, and so on). If you want to specify only content-type headers, you can configure the Multipart Content-Type property instead. This field set comprises the following fields:
|
|
| Key | String/Expression | The name of the HTTP header. Note: This property is expression-enabled. For more
information on the expression language, see Understanding Expressions in SnapLogic and Using Expressions. For
information on pipeline parameters, see Pipeline Properties.
Default value: N/A Example: content-type |
| Value | String/Expression | The value that you want to assign to the HTTP header. Note: This property is
expression-enabled. For more information on the expression
language, see Understanding Expressions in SnapLogic and Using Expressions. For
information on pipeline parameters, see Pipeline Properties.
Default value: N/A Example: application/json |
| Response entity type | Dropdown list | Select one of the following response entity types you want the Snap to display in
the output document.:
Note: If you select TEXT or BINARY, the Snap does not parse the
entity content. If you select DEFAULT, the Snap produces the
expected result in most cases, but if it fails to process as
expected, you can set the Response entity type to TEXT or
BINARY. Default value: DEFAULT Example: TEXT |
| Cookie Policy | String/Expression/ Suggestion | Select a Cookie Policy from the following options:
Default value: Ignore Cookies Example: RFC Strict |
| Read timeout | Integer | Specify the number of seconds for which the Snap waits before aborting the request
due to a failure to read from the target service.
Default value: 900 Example: 60 |
| Connection timeout | Integer | Specify the number of seconds for which the Snap waits before aborting the request
due to a failure to establish a connection to the target endpoint or
service. Default value: 30 Example: 60 |
| Maximum request attempts | Integer | Specify the maximum number of attempts that the Snap must make to receive a
response. If the attempts do not result in a response, the Snap
terminates the request. Default value: 5 Example: 3 |
| Retry request interval | Integer | Specify the time in seconds to wait before retrying the request. Default value: 3 Example: 10 |
| Retry Policy | String | Select how you want to handle connection and error responses from the following
options:
Default value: Connection errors Example: All errors |
| Normalize URL | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to normalize the Service URL. This enables the Snap to
convert double slashes (//) in the URL path to single slash (/).
For example, https://example.com/path//to//file is converted to https://example.com/path/to/file. Deselecting this checkbox reverts the Snap to 4.19 Snaplex behavior, wherein the URL paths were not normalized by default. Note: In the 4.20
release, due to the HTTP client upgrade the URL paths were
normalized by default. Hence, there was a change in behavior in
handling the URL paths in 4.20 release when compared to 4.19.
This change in behavior should not impact the existing
pipelines, because most of the websites map URL paths with
double or single slashes to the same endpoint. For example,
https://snaplogic.com/company/diversity and direct
to the same endpoint. Therefore, we recommend you to select the
Normalize URL checkbox. However, an exception to this is when you use non-standard URLs that differentiate the URL paths containing double slashes from those with single slashes and map them to different endpoints, in which case you must deselect Normalize URL checkbox. For example, http://host/pages/foo.html and http://host/pages//foo.html point to different URIs, and servers assign different meanings to them. Default value: Selected Example: Deselected |
| Has next | String/Expression | Enter the expression that must be evaluated on the output document to true
or false, to indicate whether there are more records
available. The Snap continues to read the next page until this
expression evaluates to false in the new set of output
documents. Note:
Has next is a property in the API response that indicates whether there are more records to be fetched. This property is used for the REST Get pagination feature, which retrieves 20 records at a time (referred to as a page), by default. Learn more about REST Get Pagination. To see this property in action, see Retrieve Contact Information from HubSpot or Retrieving Contact Information from HubSpot Using Upstream Values, below. Note: This field is null-safe; if the evaluated
value is null, or if there is no value provided in Has next
field, the Snap stops the pagination. Default value: N/A Example: $entity['has-more'] |
| Next URL | String/Expression | Enter the expression that is evaluated on the output document to a URL that the
Snap must use to get the next page. This property is used for the
REST Get pagination feature. The Next URL has two components, which are structured as follows:
You can create the Next URL in either of the following ways:
Here,
If the API response does not contain a field with information about the last entity retrieved, you can use the Snap's output document count to fetch the next page. For example,
Note: The Next URL is evaluated as an expression but not
encoded, which is the general behavior of the Snap.
Default value: N/A Example: $entity['has-more'] |
| Pagination interval(s) | Integer | The number of seconds for the Snap to wait before attempting to get the next page.
Default value: 0 Example: 10 |
| Show all headers | Checkbox | The REST endpoint may return a response with multiple headers with the same header name.
Note: If any of these objects has a key-value format, it is
parsed into the map data. Default value: Deselected |
| Snap execution | Dropdown list | Select one of the following three modes in which the Snap executes:
Default value: Validate & Execute Example: Validate & Execute |
REST Get Pagination
When making REST API calls to a specific endpoint using the GET method, there might be a lot of results to return. We use the pagination settings to fetch all the records/documents on multiple pages. For example, if the GET API call returns 20 documents by default, to get all other pages/records, we use Has Next field and get the list of all records until the last record.
Using REST Get to Process gzip Compressed Data
The response can provide gzipped data. In that case, the Snap can be configured to process it using the header parameter:
HTTP Header
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| Accept-Encoding | gzip |
| Accept | */* |
The stream is then uncompressed while parsing the data and making it available on the output view.
Troubleshooting
Failed to execute HTTP request
Reason: The Service URL must have a protocol, such as
http:// or https://. <Service_URL>:
Name or service not known. This basically means that the service URL you
entered is not accessible.
Resolution: Check the Snap properties. Specifically, check your entry in the Service URL field.
Failure: Validation errors: property_map.settings.serviceUrl.value: Could not compile expression: <Service_URL>
This
means that you have turned expressions on () while entering string
value into the Service URL field.
Resolution:Fix the snap configuration and try executing again.
Please check expression syntax. Ensure that your service URL is a proper
expression; or turn off the expression control () .
URL Parse Exception - 403
Reason: The Service URL path might be containing any of the following special characters: !, =, %, #, $, ^&()_¢äâêîôûñç¡¿ÉÙËǨ°¸ðø©¢¾A+²½µ®§÷¶þ
Resolution: To escape the special characters, use the global function encodeURIComponent on any variables that might contain special characters so that they are encoded properly.
Too many Requests - 429
Reason: There are too many requests to REST endpoint.
Resolution:Wait for the retry to succeed. Rest related Snaps extract the response header and automatically retry when they encounter status 429.
By default, the retry interval (Retry-After) is specified in the HTTP response header. If no value is available for Retry-After, then the Snap’s Retry Interval value is used.
Example
- Create and Delete an Account in SnapLogic Using REST Snaps
- Retrieve Contact Information from HubSpot
- Retrieving Contact Information from HubSpot Using Upstream Values
- Connect to the SnapLogic API
- Connect to rally with REST
- REST Get pagination: Eloqua and Marketo
- Handles Multiple Response Cookies
- When Process Array is Selected or Deselected


