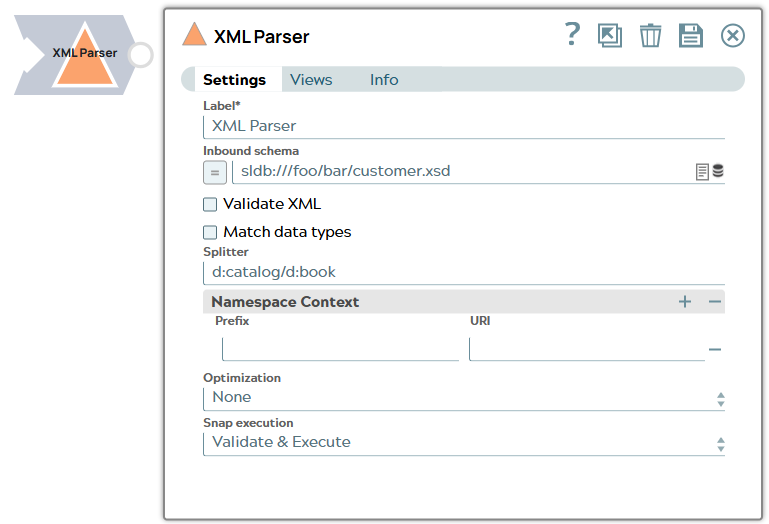
XML Parser
Overview
You can use this Snap to parse the incoming XML data into SnapLogic document objects. The supported schema language is: W3C XML Schema 1.0
Parse-type Snap
Works in Ultra Tasks
Limitations
The XML Parser Snap does not support mixed content, such as the following XML data, because it may contain attributes, elements, and text.
<letter>
Dear Mr. <name>John Smith</name>.
Your order <orderid>1032</orderid>
will be shipped on <shipdate>2001-07-13</shipdate>.
</letter>Snap views
| View | Description | Examples of upstream and downstream Snaps |
|---|---|---|
| Input | The input must be:
The input must be properly structured XML data without mixed content elements for the XML Parser to process it correctly. Example of Valid Input |
|
| Output |
Each XML element is converted into a corresponding field in the output document. The output maintains the hierarchical structure of the original XML. It can be processed by any downstream Snap that accepts document input. |
|
| Error |
Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter when running the pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab. The available options are:
Learn more about Error handling in Pipelines. |
|
Snap settings
- Expression icon (
): Allows using pipeline parameters to set field values dynamically (if enabled). SnapLogic Expressions are not supported. If disabled, you can provide a static value.
- SnapGPT (
): Generates SnapLogic Expressions based on natural language using SnapGPT. Learn more.
- Suggestion icon (
): Populates a list of values dynamically based on your Snap configuration. You can select only one attribute at a time using the icon. Type into the field if it supports a comma-separated list of values.
- Upload
 : Uploads files. Learn more.
: Uploads files. Learn more.
| Field / Field set | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Label | String | Required. Specify a unique name for the Snap. Modify this to be more appropriate, especially if more than one of the same Snaps is in the pipeline. Default value: XML Parser Example: XML Parser |
| Inbound schema | String/Expression | XSD schema definition file url for the incoming data. The currently supported
url protocols are SLDB, HDFS, S3. Important: If you enter an Inbound
schema, then you must select Validate XML and Match data types
properties to derive the output as per the defined schema. Default value: None Example: sldb:///foo/bar/customer.xsd |
| Validate XML | Checkbox |
Required. Appears when you enable expression for Inbound schema. If selected, the incoming data will be validated against the provided XSD schema definition. Note: If you enter an Inbound schema, then you must select Validate
XML and Match data types properties to derive the output as per the
defined schema.
Default status: Deselected |
| Match data types | Checkbox |
Select this checkbox to convert the output document data types to the data type as specified in the inbound schema property. Note:
Default status: Deselected |
| Splitter | String | Specify the value to split the incoming XML document into multiple smaller
documents using the XPath expression. Note: This expression must be of the form
a/b/c/d or ns1:a/ns2:b/ns3:c/ns4:d where the
prefixes ns1 to 4 can be the same or different. Learn more.Default value: None. Example: d:catalog/d:book |
| Namespace Context |
Optional. Namespace context for the expression provided in the Splitter property. Namespaces are typically defined in the format of xmlns prefix:URI |
|
| Prefix | String | Prefixes included in the expression provided in the Splitter property. |
| URI | String | URIs associated with the prefixes. |
| Optimization | Dropdown list | Select the parameter that you want to optimize during Snap execution. Available options:
Default value: None. |
| Snap execution | Dropdown list |
Choose one of the three modes in
which the Snap executes. Available options are:
Default value: Execute Only Example: Validate and Execute |
Spiltters
Splitter expression without prefix
Example: breakfast_menu/food
Default namespace can be accessed by giving a unique prefix in the splitter expression followed by a colon and the tag value. Provide its corresponding namespace value in the Prefix URI table. Ensure this prefix is not used in the XML before using it.

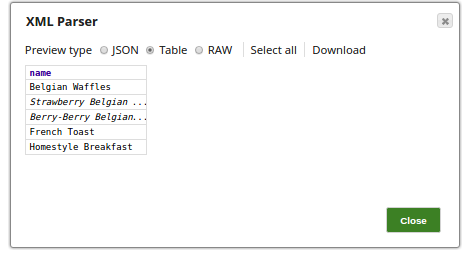
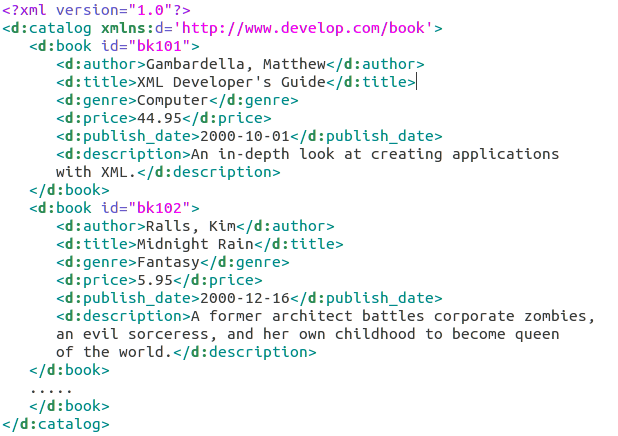
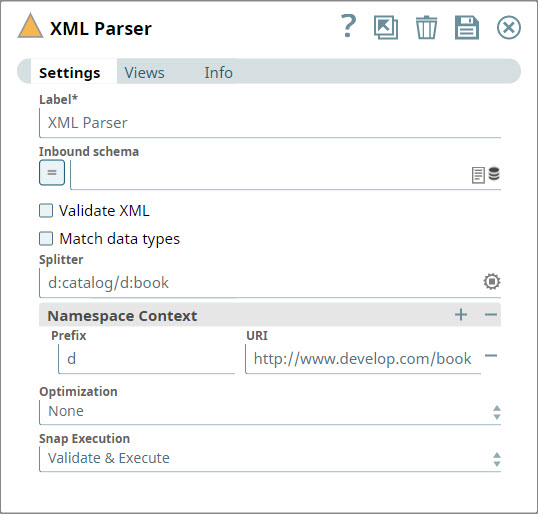
Splitter expression with prefix
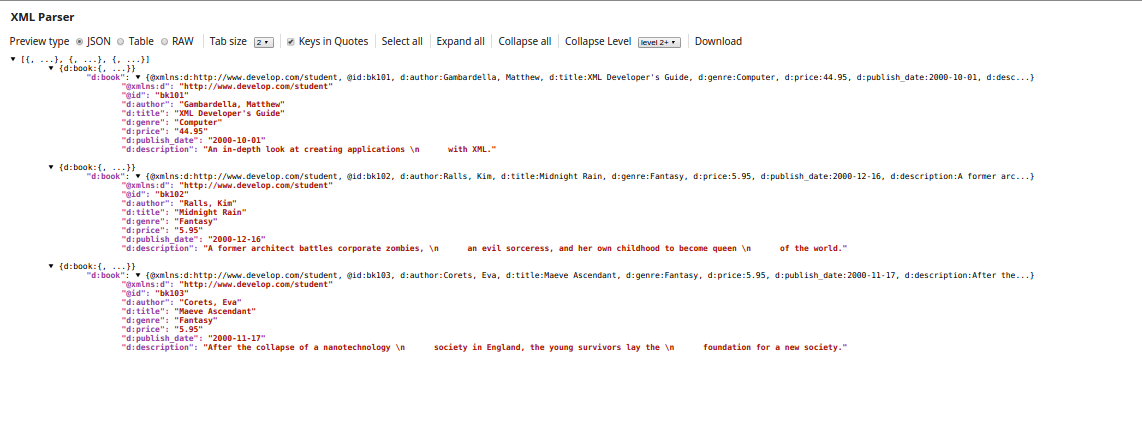
Example: d:catalog/d:book
For the Splitter expression: "d:catalog/d:book”, the output contains two
output documents—one for each note tag in the XML file. If the Splitter expression contains
prefixes, they must be defined in the Namespace Context.
| Prefix | URI |
|---|---|
| d | http://www.develop.com/student |
Troubleshooting
| Error | Reason | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| "Failed to convert xml to json" | "Unexpected character." | Ensure that the xml data is well formed. |


