Error handling in Snaps
An error pipeline is beneficial when a user seeks to standardize the error-handling behavior across a project or multiple projects.
Benefits of using error pipeline
-
Isolation of errors: Errors are isolated from the main processing flow, preventing them from disrupting the entire pipeline. This ensures that your pipeline can continue working with valid data.
-
Custom error handling: You can design the error pipeline to handle errors in a way that makes sense for your specific use case. This may involve logging, data transformation, or even sending notifications.
-
Better monitoring and troubleshooting: By routing errors to a dedicated error pipeline, you can easily monitor and troubleshoot issues. You can log error details, capture relevant context, and take corrective actions.
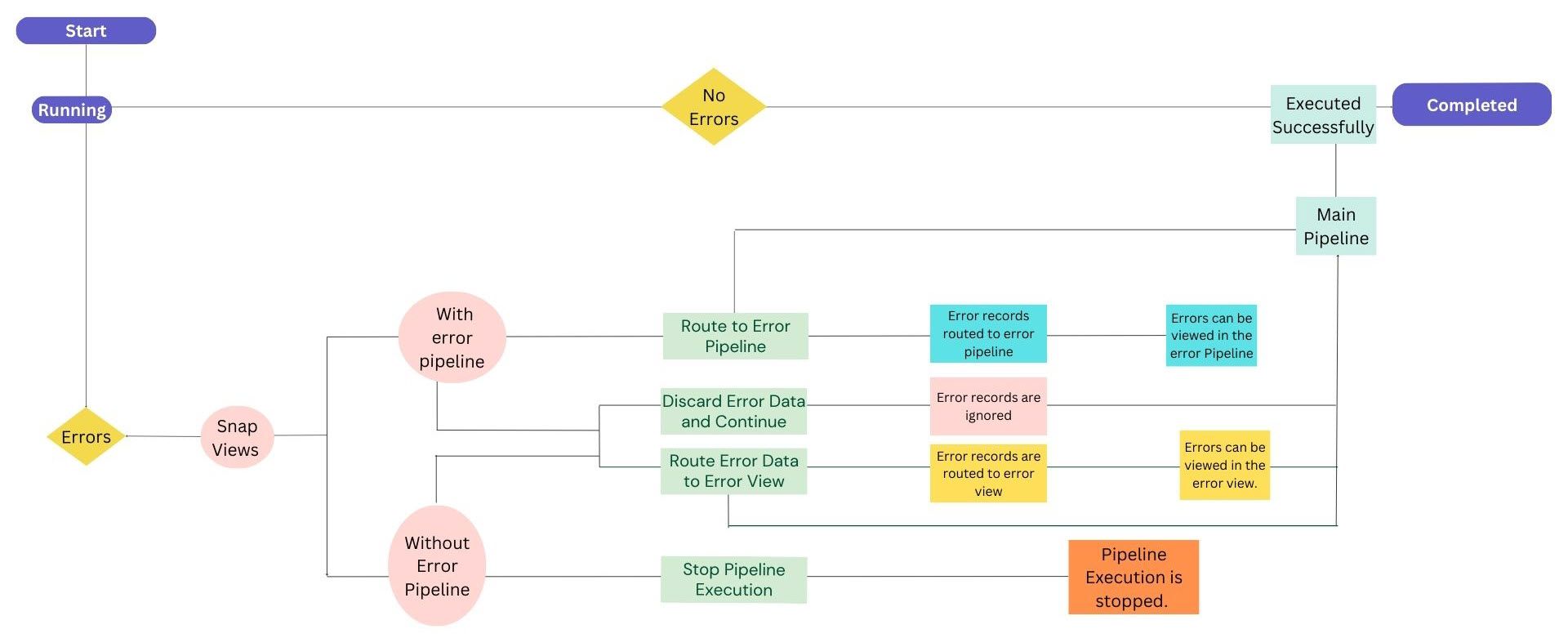
The following infographic displays the step-by-step workflow of error handling in Snaps and how the status of the pipeline changes when errors are encountered.
Best practices when using an error pipeline
When developing an error-handling solution, it's crucial to consider various factors to ensure its effectiveness. Follow these steps to create a reusable error-handling pipeline that not only identifies errors promptly but also streamlines communication and minimizes effort across teams. Ensure that you follow these best practices while creating the error pipeline:
-
Pipeline reusability:
Ensure the error-handling pipeline is designed for maximum reusability.
Parameterize the pipeline to enable dynamic invocation across multiple projects.
-
Structural integrity:
Structurally organize the error handling pipeline to minimize the effort required for modifications.
Prioritize a well-structured design for ease of maintenance.
-
Optimized performance:
Strive for optimal performance in the error-handling process.
Enhance execution efficiency to minimize processing time.
-
Effective process handling:
Implement best practices for storing error data to expedite error identification.
Create error files and store them in various locations such as SFTP/FTP, SMB, SLDB, local file system, Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, etc.
Send email notifications to relevant groups based on the type of error and team responsibilities for a specific issue.


