XML Formatter
Overview
You can use this Snap to format the incoming document objects into XML data format.
Breaking Change for Pipelines Using the XML Formatter Snap
After upgrading to 425patches10152, the Snap might fail when you select Map input to first repeating element in XSD checkbox with an Could not convert the document to an XML error. In such cases, ensure that you provide a complete path from the root element for an object and map the input properly to the root element.
Format-type Snap
Works in Ultra Tasks if Root element property is not selected.
Snap views
| View | Description | Examples of upstream and downstream Snaps |
|---|---|---|
| Input | The input data must be in document format. The Snap accepts document objects as input and formats them into XML data format. You can specify an Outbound schema (XSD file URL) to define the structure of the outgoing XML data. | |
| Output | The Snap produces XML document in binary format.
Note: Attributes with null values are not displayed in XML output.
|
|
| Error |
Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter when running the pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab. The available options are:
Learn more about Error handling in Pipelines. |
|
Snap settings
- Expression icon (
): Allows using pipeline parameters to set field values dynamically (if enabled). SnapLogic Expressions are not supported. If disabled, you can provide a static value.
- SnapGPT (
): Generates SnapLogic Expressions based on natural language using SnapGPT. Learn more.
- Suggestion icon (
): Populates a list of values dynamically based on your Snap configuration. You can select only one attribute at a time using the icon. Type into the field if it supports a comma-separated list of values.
- Upload
 : Uploads files. Learn more.
: Uploads files. Learn more.
| Field / Field set | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
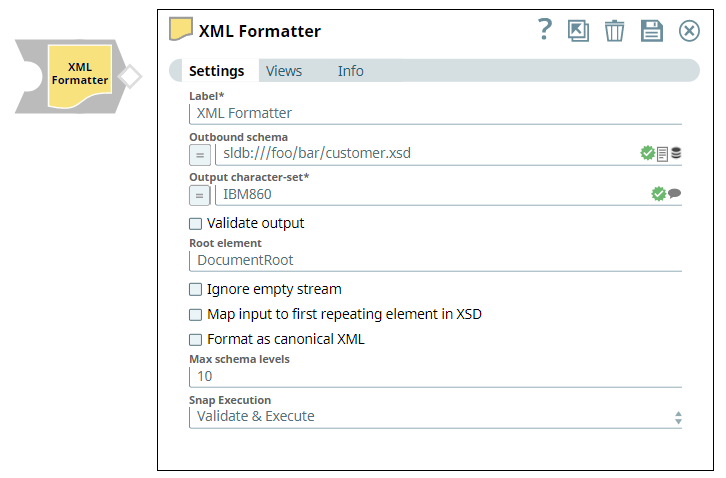
| Label | String | Required. Specify a unique name for the Snap. Modify this to be more appropriate, especially if more than one of the same Snaps is in the pipeline. Default value: XML Formatter Example: XML Formatter |
| Outbound schema | String/Expression | Specify the XSD schema definition file URL for the outgoing data. The currently
supported URL protocols are SLDB, HDFS, S3. The Schema language supported is W3C XML Schema 1.0. Default value: N/A Example: sldb:///foo/bar/customer.xsd |
| Output Character Set | String/Expression/ Suggestion | Required. Specify or select the character set encoding for the output. 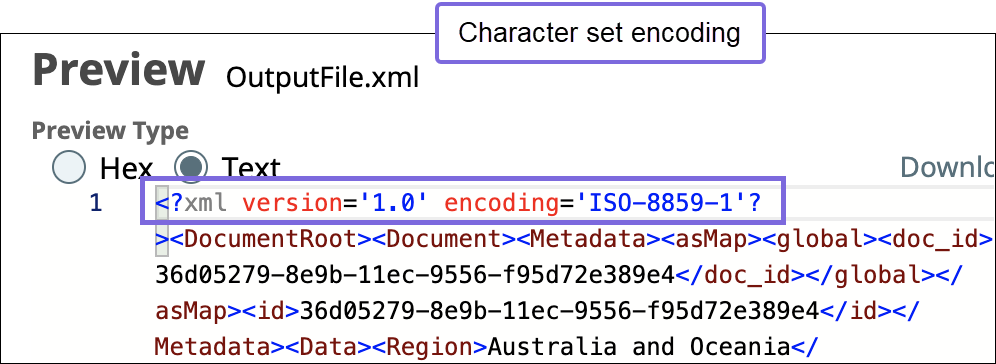 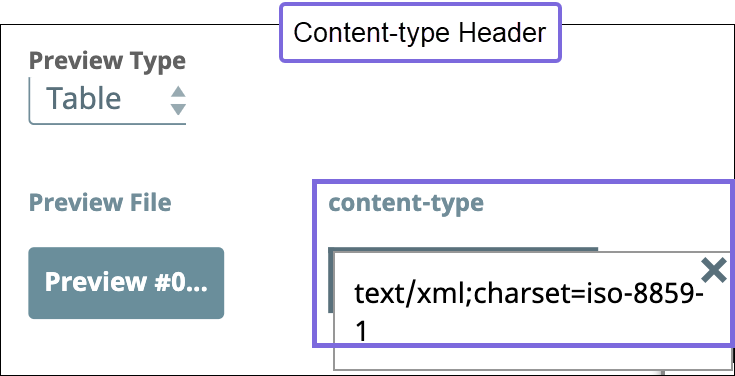 Default value: UTF-8 Example: ISO860 |
| Validate output | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to validate the output against the provided XSD schema
definition in Outbound Schema field. Important: If you enter an
Outbound schema, then you must select Validate XML and Match
data types checkboxes to get the output as per the defined schema.
Default status: Deselected |
| Root element | String | Specify the name of the XML element under which all the incoming documents are added. If left blank, no wrapping is done and each document is written out as a separate binary. Default value: None. Example: DocumentRoot |
| Ignore empty stream | Checkbox |
Select this checkbox to enable the Snap to ignore when no document is received in the input view. Deselect this checkbox to enable the Snap to write an empty XML data with a header at the output view when no document has been received in the input view. Default status: Deselected |
| Map input to first repeating element in XSD | Checkbox | Select this checkbox if you want the Snap to ignore the root element from the
XSD file. See the example below for more information. Note: This is applicable only when the Snap has the repeated element such as
Array in the XSD.
If this property is selected, the root element property is ignored and the <Metadata> ... </Metadata> element does not appear at the output. If this property is not selected, the Snap writes the XML data and the input document data is always wrapped in <Data> ... </Data>. If there is no root element, map the input to the root element. Default status: Deselected |
| Format as Canonical XML | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to transform the XML output to canonical XML. The canonical form of an XML output (from XML Formatter Snap) is an XML representation that excludes the XML prolog and includes the start and end tag for all the XML elements. Learn more about Canonical XML Version 1.0 specifications: https://www.w3.org/TR/xml-c14n. Default status: Deselected |
| Max schema levels | String | Specify the max levels for schema to be processed by the Snap. This configuration limits the number of schema levels provided by the outbound schema on the SnapLogic input view to a maximum of 10 levels. This configuration does not effect the validation capability. It serves to prevent outbound schemas from consuming too much memory and processing time. Default value: 10 Example: 20 |
| Snap execution | Dropdown list |
Choose one of the three modes in
which the Snap executes. Available options are:
Default value: Validate and Execute Example: Execute only |
Additional information
The conversion from the internal JSON structure to XML follows the StAXON mapping convention. This mapping uses naming conventions to turn JSON object fields into XML nodes and attributes.



will be transformed into <msg attr1="0"/>.

If you want to generate a file without the wrapper elements, you can remove the "Root Element" property and the Snap produces a single binary document for every input document. The Snap also validates documents against a provided schema to ensure that the output is well-formed. Any invalid documents will be written to the error output view.
XML Formatter and XML Generator Output Differs for the Same XSD File Input
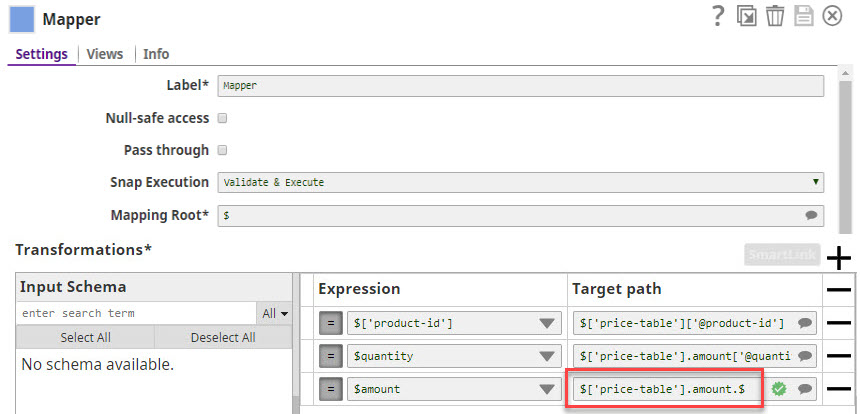
- XML Formatter : .$
-
XML Generator
: .value