File Writer
Overview
You can use the File Writer Snap to read a binary data stream from the input view and write it to a specified file destination. Possible file destinations include: SLDB, HTTP, S3, FTP, SFTP, FTPS, or HDFS. If you provide file permissions for the file, the Snap sets those permissions to the file.
You must install the AzCopy utility, if you use the ABFS (Azure Blob File Storage) file protocol Azure Data Lake Gen 2 for bulk operation. The utility must be installed in Snaplex to fetch the file path. If the path is null, the native Azure Storage SDK is used for all operations. Learn more about the AzCopy command. If AzCopy Utility is not installed for ABS file transfer, the file transfer will not be as fast as using AzCopy because a REST call will be invoked for each file content instead of a bulk operation.
The SnapLogic Platform does not support the installation of utilities or processes on Cloudplexes. Learn more.
We plan to introduce additional S3 features exclusively in Amazon S3 Snaps, while Binary Snaps with S3 support will not contain these updates. Therefore, we recommend you to use the Amazon S3 Snap Pack for all your S3 operations within your pipelines. However, Binary Snaps will be retained as is to maintain backward compatibility, but be aware that we will no longer provide S3 support for the Binary Snaps.
Learn more: Migrate from Binary to S3 Snaps.

Write-type Snap
Works in Ultra Tasks
Prerequisites
The 'IAM_CREDENTIAL_FOR_S3' feature is used to
access S3 files from EC2 Groundplex, without Access-key ID and Secret key in the AWS S3
account in the Snap. The IAM credential stored in the EC2 metadata is used to gain access
rights to the S3 buckets. To enable this feature, set the Global properties (Key-Value
parameters) and restart the JCC:jcc.jvm_options =
-DIAM_CREDENTIAL_FOR_S3=TRUE
This feature is supported in the EC2-type Groundplex only. Learn more.
Limitations
- Files uploaded to SLFS have a 100-MB per file limit. This limit does not apply when writing to external storage.
- Do not use SLDB as a file system or storage. File Assets are intended only for specialized files that a pipeline uses to reference certain data, such as accounts, expressions, or JAR files. Use a Cloud storage provider to store production data. File Assets should not be used as a file source or as a destination in production pipelines. When you configure the Writer Snaps, set the file path to a cloud provider or external file system.
Known issues
-
The Snap creates a zero-byte file when writing a file to FTPS server (FileZilla) using TLS v1.3 for FTPS (explicit FTP over TLS) and FTPIS (implicit mode) modes. Note that this is an intermittent issue. By default, the Snap uses TLS v1.3.
Workaround: To prevent the Snap from writing zero-byte files, use TLS v1.2. To use TLS v1.2, you must set the following jcc.jvm options in the Global properties of your Snaplex:
Key:
jcc.jvm_optionsValue:
-DFTPS_SSL_TLS_PROTOCOL=TLSv1.2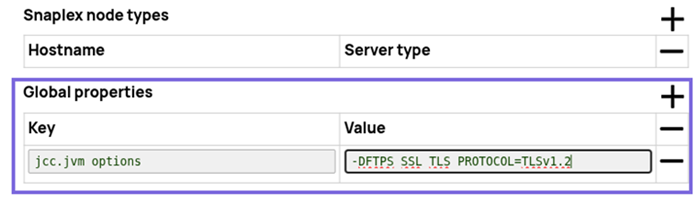
-
This Snap Pack no longer natively supports RSA-SHA1 authentication with the Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP). To enable support for RSA-SHA1 authentication, set the following property in the Node Properties, Learn more: Configuration Options:
-Djsch.server_host_key=ssh-rsa -Djsch.client_pubkey=ssh-rsa - This Snap does not create an output file when using the input from SAS Generator Snap configured with only the DELETE SAS permission. This is not the case when the target file exists.
- This Snap does not fail and turns green after execution despite providing an expired SAS URI. As a workaround, select Validate after write to fail the Snap in case of invalid credentials.
- This Snap Pack does not natively support SHA1-based algorithms to connect to SFTP endpoints. With the August 2023 GA release, you can now leverage the properties specified in the Configuration settings for Snaps to add support for ones that are disabled on your Snaplex.
Snap views
| View | Description | Examples of upstream and downstream Snaps |
|---|---|---|
| Input | Any binary data stream. |
|
| Output | The output view for this Snap is optional. If an output view is open and the
file write action is successful, the output view provides a document with
information on the filename, result, and original data. An example is: |
|
| Error |
Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter when running the pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab. The available options are:
Learn more about Error handling in Pipelines. |
|
Snap settings
- Expression icon (
): Allows using pipeline parameters to set field values dynamically (if enabled). SnapLogic Expressions are not supported. If disabled, you can provide a static value.
- SnapGPT (
): Generates SnapLogic Expressions based on natural language using SnapGPT. Learn more.
- Suggestion icon (
): Populates a list of values dynamically based on your Snap configuration. You can select only one attribute at a time using the icon. Type into the field if it supports a comma-separated list of values.
- Upload
 : Uploads files. Learn more.
: Uploads files. Learn more.
| Field / Field set | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Label | String | Required. Specify a unique name for the Snap. Modify this to be more appropriate, especially if more than one of the same Snaps is in the pipeline. Default value: File Writer Example: File Writer |
| File name | String/Expression | Required. Specify the URI of the destination file to
which the data (binary input from the upstream input view) is written. It may start
with one of the following protocols:
Learn more : Note:
Warning:
Learn more : Additional Information Warning: Lint Warning The Snap displays a Lint Warning in your
Pipeline in the following scenarios:
Therefore, we recommend that you conform to any of the acceptable
relative paths. Otherwise, use an absolute path—that is provide a file path that
belongs to the same org where you want to write the file, or use the File Upload
Note:
Writing Files in S3 To write files in S3, your account must have full access. Default value: None. Examples:
|
| Prevent URL encoding | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to use the file path value as-is without encoding the URL.
This prevents the Snap from encoding the file path URL (including the query string
if any) automatically. Deselect this checkbox to automatically encode the characters
in the File URL. Refer : Encoding of Characters in a URL Default status: Deselected |
| File action | Dropdown list | Specify the action to perform if the file already exists. The available options are:
Warning:
Note: The Append operation is supported for FILE, SFTP, FTP, and FTPS
protocols only. For any other protocols that are not supported by Append,
we recommend that you use the
File Operation
,
File Writer
, and
File Delete
Snaps and follow this
procedure.
Note: This approach might involve disk overhead, therefore ensure
that you have enough disk space in your system.
Default value: Overwrite Example: Overwrite |
| Write empty file | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to write an empty file when the incoming binary document
has empty data. If there is no incoming document at the input view of the Snap, no
file is written regardless of the value of the property. Default status: Deselected |
| Write header file | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to allow the Snap to write a header file by appending
".header" to the value of the File name property. The same header information is
also included in the output view data, as shown in the "Expected output" section
above, under the key original. Warning:
Default status: Deselected |
| Validate after write | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to enable the Snap to check if the file exists after the
completion of the file write. This may delay a few more seconds for the
validation. Default status: Deselected |
| Number of retries | Integer/Expression | Specify the maximum number of retry attempts to make when the Snap fails to
write. If the value is larger than 0, the Snap first stores the input data in a
temporary local file before writing to the target file. Note:
Minimum value: 0 Default value: 0 Example: 3 |
| Retry interval (seconds) | Integer/Expression | Specify the minimum number of seconds for which the Snap must wait before
attempting recovery from a network failure. Minimum value: 1 Default value: 1 Example: 3 |
| File permissions for various users | Use this field set to provide any combination of
permissions to the available users. Warning:
|
|
| User type | String/Expression/ Suggestion | Choose one of the three standard user types. The available options are:
Each row can have only one user type and each user type should appear only once. Select one from the suggested list. Specify at most one row per user type. Default value: N/A Example: owner |
| File permissions | String/Expression/ Suggestion | Specify the privilege to provide to the user on the file. The available
permissions are:
Default value: N/A Example: read + write + execute |
| Create directory if not present | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to enable the Snap to create a new directory if the
specified directory path does not exist. This field supports FTP, SFTP, and SMB
protocols—these protocols allow creation of directories when they are not present.
However, this field does not support HTTP, HTTPS, and SLDB file protocols. Note:
Default status: Deselected |
| Flush interval (kB) | Integer |
Specify the flush interval in kilobytes during the file upload. Note: The Snap can flush a given size of data output stream written to the target
file server. If the value is zero, the Snap flushes in maximum frequency after
each byte block is written. Larger the value is, the less frequent flushes the
Snap performs. Leave the property at default -1 for no flush during the upload.
This property may help if the file upload experiences an intermittent failure.
However, more frequent flushes will result in a slower file upload.
Default value: -1 Example: 100 |
| Advanced properties | Use this field set to add advanced properties, such as SAS URI. | |
| Properties | String | The URI of the Shared Access Storage (SAS) to be accessed. Supported SAS types are::
Default value: SAS URI Example: SAS URI |
| Values | String/Expression |
Specify the value for the SAS URI. Warning: When you specify the SAS URI value in the Snap settings, then
the settings provided in the account (if any account is attached) are
ignored.
Default value: N/A Example: https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/sascontainer/sasblob.txt?sv=2015-04-05&st=2015-04-29T22%3A18%3A26Z&seD |
| AWS Canned ACL | Dropdown list |
This field appears only when your account type is set to AWS S3. Select the predefined ACL grant (from AWS) to use when writing a file to S3.
Choose a Canned ACL from the available options:
Watch the video below for more information about AWS Canned ACL. Learn more: AWS Canned ACLs. Default value: None. Example: PublicRead |
| Snap execution | Dropdown list |
Choose one of the three modes in
which the Snap executes. Available options are:
Default value: Execute only Example: Validate & Execute |
Syntax for writing files
-
For SL DB: <filename>.<file extension>. For example,
employee_details.json,contacts.csv -
For S3: S3\\<project name>\\folder. For example,
s3://snaplogic/test -
For Staging: stageName. For example, public.my_s3_stage
Acceptable File Paths
- Relative paths
filename.json: Saves the file in the project.../shared/filename.json: Saves the file in the Project Shared Space.../../shared/filename.json: Saves the files in the Org Shared project.
- Absolute path
-
/<org>/<projectSpace>/<project>/filename.json
-
Writing Files in SLDB
-
If you enter a file name, such as file.csv, then it writes the file to:
/<org>/projects/<pipeline project>/file1.csv(where <org> is your organization name and <pipeline project> is the project where the Pipeline is stored), if the Pipeline is in a project other than the shared project. -
If you enter shared/file1.csv, then it writes the file to:
/<org>/shared/file1.csv.
The Snap can write a file to its own project directory or the shared project, and cannot write it to another project directory.
File Patterns
- A key-value pair with "filename" key can be defined as a Pipeline parameter:
_filename - If the Snap is executed in the Windows Groundplex and needs to access D: drive, the
format should be:
file:///D:/testFolder/ - To write 'sample.csv' file into the 'testDir' folder in the 'Snaplogic' container:
wasb:///snaplogic/testDir/sample.csv - To read 'test.csv' file in the 'csv/' folder of the 'mybucket' bucket):
gs:///mybucket/csv/test.csv -
For region names and their details, see AWS Regions and Endpoints.
Example: s3:///[email protected]/test.json - Ensure the file name does not contain '?' character, because it is not supported. The Snap fails with an error if you include the '?' character.
Reading files from Project and Shared Project Spaces
- If a Pipeline is created in a project other than the shared project and you want to read
the
"asset.json"file from the same project, enter"asset.json" or "sldb:///asset.json". - If a Pipeline is created in the shared project and you want to read the
"asset.json"file from the shared project, enter"asset.json"or"sldb:///asset.json". - If a Pipeline is created in a project other than the shared project and you want to read
the
"asset.json"file from the shared project, enter"shared/asset.json"or"sldb:///shared/asset.json". - Ensure the file name, folder name, or the file path does not contain '?' character because it is not fully supported and when present, the Snap might fail.
Encoding of characters in a URL
Following are some of the common characters that are automatically encoded.
| Character | Character Name | URL Encoded value |
|---|---|---|
| backlash | \ | %5c |
| pound | # | %23 |
| space | %20 | |
| percent | % | %25 |
| Left-angle | < | %3C |
| Right-angle | > | %3E |
| Left-square | [ | %5B |
| Right-square | ] | %5D |
| Left-curly | { | %7B |
| Right-curly | } | %7D |
Following are some of the characters that are not automatically encoded by the Snap:
| Character | Character Name | URL Encoded value |
|---|---|---|
| semi-colon | ; | %3B |
| question-mark | ? | %3F |
| forward-slash | / | %2F |
| colon | ; | %3A |
| ampersand | & | %26 |
| equals | = | %3D |
| plus | + | %2B |
| dollar | $ | %24 |
| comma | , | %2C |
Video Demonstration
- The following video helps to understand the new AWS canned ACL property.
Additional Information
You can also access the fields in a binary header when specifying a file name. For example,
if you have a File Reader Snap upstream of a File Writer Snap, you can access the
"content-location" header field to get the original path of the file. You can then use a new
file name based on the old one, for instance, to make a backup
file:$['content-location'].match('/([^/]+)$')[1] + '.backup'
For http: and https: protocols, the Snap uses http PUT method only. This property should have the following syntax:
[protocol]://[host][:port]/[path]
"://"is a separator between the file protocol and the rest of the URL and the host name and the port number should be between"://"and"/". If the port number is left empty, a default port number for the protocol is used. The hostname and port number are left empty in the sldb and S3 protocols. The value in this field should be an absolute path for all protocols except SLDB.-
When using the file:/// protocol, the file is accessed based on the permissions of the user associated with the Snaplex (Default: Snapuser).
-
For HDFS, if you want to be able to suggest information, use the HDFS Writer Snap.
Use the file system access with caution, and ensure to clean up the file system after use.
Troubleshooting
| Error | Reason | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
Algorithm negotiation fail: algorithmName="server_host_key"
jschProposal="<algorithms>" serverProposal="ssh-rsa" |
The library that we use for SFTP connections no longer supports deprecated signature protocols by default. (This changed with the 4.33 GA release.) | Add the algorithm to the serverProposal in the global.properties file. You
can also enable support for RSA-SHA1 authentication in the Node
Properties tab on the Updating a Snaplex
dialog in SnapLogic Manager.
Learn more: Configuration Options |
| Could not evaluate expression: filepath Mismatched input ':' expecting {<EOF>, '||', '&&', '^', '==', '!=', '>', '<', '>=', '<=', '+', '-', '*', '/', '%', '?', '[', PropertyRef}. |
The expression toggle (=) is selected on the File name field, so it is trying to evaluate the file path as an expression. |
Check the expression syntax. Disable the expression toggle to remove the field out of expression mode. |
|
Failure: filename is undefined filename was not found in the containing object. |
The expression toggle (=) is selected on the File name field, so it is trying to evaluate the filename as an expression. |
Check expression syntax and data types. Disable the expression toggle to remove the field value out of expression mode. |


