Generic JDBC Database Account
Overview
You can use this account type to connect JDBC Snaps with data sources that use the Generic JDBC Database Account .
Known issues
Generic JDBC Snaps connecting to the Informix database through the Generic JDBC Database Account can cause thread leaks because of JDBC driver implementations.
- Use the Informix JDBC driver 4.50.4.1 version or a later version.
- Configure the following URL properties in the account settings:
- Url Property name: IFMXCONNECTION_CLEANER_THREADS
- Url property value: 0
Your existing pipelines that use JDBC Snaps to integrate with Oracle or Redshift databases using the bundled Oracle or Redshift JDBC drivers will stop functioning with the 438patches28052.
Workaround
You must manually upload the Oracle or Redshift JDBC driver in the JDBC Database account to run your pipelines successfully.
Download the drivers:
OJDBC: Maven Repository: com.oracle.database.jdbc » ojdbc6 » 11.2.0.4
Redshift: Maven Repository: com.amazon.redshift » redshift-jdbc42 » 2.1.0.11
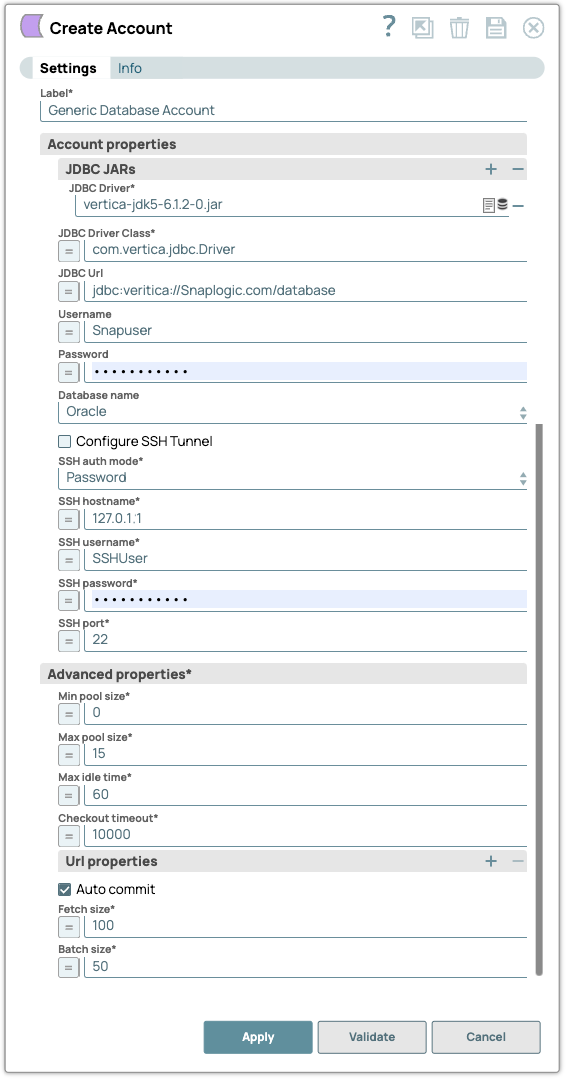
Account settings
- Expression icon (
): Allows using JavaScript syntax to access SnapLogic Expressions to set field values dynamically (if enabled). If disabled, you can provide a static value. Learn more.
- SnapGPT (
): Generates SnapLogic Expressions based on natural language using SnapGPT. Learn more.
- Suggestion icon (
): Populates a list of values dynamically based on your Snap configuration. You can select only one attribute at a time using the icon. Type into the field if it supports a comma-separated list of values.
- Upload
 : Uploads files. Learn more.
: Uploads files. Learn more.
| Field / Field set | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Label | String |
Required. Specify a unique label for the account. Default value: N/A Example: Generic Database Account |
| Account Properties | The information required to create a connection to the database. | |
| JDBC JARs | Use this field set to define JDBC Drivers. This field set consists of the JDBC Driver field. | |
| JDBC Driver | String | Required. Specify the JDBC driver to use. Click on the
Upload Note:
Default value: N/A Example: vertica-jdk5-6.1.2-0.jar |
| JDBC Driver Class | String/Expression | Required. Specify the JDBC Driver class name to use. Default value: None. Example: com.vertica.jdbc.Driver |
| JDBC URL | String/Expression | Specify the JDBC URL to use. Default value: None. Example: jdbc:vertica://Snaplogic.com/database |
| Username | String/Expression | Specify the database username to use. Default value: N/A Example: Snapuser |
| Password | String/Expression | Specify the database password to use. Default value: N/A Example: nb*#!@09 |
| Database name | Dropdown list |
Choose a database to which the account must be connected. The available
options are:
Note:
Default value: Auto detect Example: Oracle |
| Test Query | String/Expression | Activates on selecting Auto detect for Database name. Specify a custom query to validate the database connection. Note:
Default value: N/A Example:
|
| Configure SSH tunnel | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to connect to the database server through the SSH tunnel.
After the operation is completed, the tunnel is closed. Learn more about SSH Tunneling with PostgreSQL Default status: Deselected |
| SSH auth mode | Dropdown list | Required. Select an option to specify the mode for
authenticating the user on the SSH tunnel. The available options are:
Default value: Password Example: KeyFile |
| SSH hostname | Integer/Expression | Required. Specify the IP address or the domain name of
the SSH server to which you want to connect. Default value: N/A Example: 127.0.0.1 |
| SSH username | String/Expression | Required. Specify the SSH username that is
authorized to connect to the database. This username is used as the default username
when retrieving connections. Note: The username must be valid to set up the data
source. Default value: N/A Example: SSHUser |
| SSH password | String/Expression | Appears if SSH Auth Mode is Password. Required. Specify the password for the SSH username for connecting to the SSH tunnel. Default value: N/A Example: <Encrypted> |
| Private key file URL | String/Expression | Appears if SSH Auth Mode is KeyFile (Private Key File). Specify the location of the private key file. The file can be in SLDB, on the host machine that is hosting the JCC, or at any other remote location. Click the File browser icon to upload the file from your local system. You can also upload the file using any protocol such as HTTPS, FTP, SLDB, and SFTP. Default value: N/A Example: postgres-ssh.pem |
| Private key | String/Expression | Appears if SSH Auth Mode is KeyFile (Private Key
String). Specify the private key for authentication. Default value: N/A Example: -----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- ……………….. -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY---- |
| Private key passphrase | String/Expression | Appears if SSH Auth Mode is KeyFile. Specify the passphrase that is to be used to decrypt the private key. Default value: N/A Example: 3x@mpl3_P@ssw0rd! |
| SSH port | Integer/Expression | Required. Specify the SSH port to connect to any of the
following database servers:
Note: Ensure that there are no port conflicts. Default value: N/A Example: 222 |
| Advanced properties | ||
| Min pool size | Integer/Expression | Required. Specify the minimum number of idle connections
a pool should maintain at a time. Note: If the size is set to non-zero, JCC restart
is needed when the database account expires. Default value: 0 Example: 0 |
| Max pool size | Integer/Expression | Required. Specify the maximum number of idle connections
a pool should maintain at a time. Default value: 15 Example: 10 |
| Max lifetime (minutes) | Integer/Expression | Required. Specify the number of minutes a
connection must remain in the connection pool before being discarded. Default value: 60 Example: 100 |
| Checkout timeout (milliseconds)* | Integer/Expression | Required. Specify the number of milliseconds to wait for
a connection to be available in the pool. Note: If you provide 0, the Snap
waits infinitely until the connection is available. Therefore, we recommend you
not to specify 0 for Checkout Timeout. Default value: 1000 Example: 10000 |
| Url properties | Use this field set to define URL properties to use in the JDBC URL. | |
| Url property name | String | Specify a name for the URL property to be used by the account. For instance:
Default value: N/A Example:
|
| Url property value | String | Specify a value for the URL property name. Default value: N/A Example:
|
| Auto commit | Checkbox | Select one of the options for this property to override the state of the Auto
commit property on the account. The Auto commit at the Snap-level has three values:
True, False, and Use account setting. The expected functionality for these modes are:
Note:
Warning: Behavior of DML Queries in Database Execute Snap when
auto-commit is false DDL queries used in the Database Execute Snap will be committed by the Database itself, regardless of the Auto-commit setting. When Auto commit is set to false for the DML queries, the commit is called at the end of the Snap's execution. The Auto commit needs to be true in a scenario where the downstream Snap does depend on the data processed on an Upstream Database Execute Snap containing a DML query.When the Auto commit is set to the Use account setting on the Snap, the account level commit needs to be enabled. Default status: Selected |
| Fetch size | Integer/Expression | Required. Specify the number of records to
retrieve from the DB at a time. Default value: 100 Example: 100 |
| Batch size | Integer/Expression | Required. Specify the number of query
statements to execute at a time. SELECT queries are not batched.
Note: If you are using AWS Athena database, the Batch size must be set to
1. Default value: 50 Example: 10 |
Troubleshooting
| Error | Reason | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
Caused by: java.lang.AbstractMethodError |
Snap displays this error when the endpoint database driver lacks an implementation for the isValid() or any other method. | To address this issue, consider the following troubleshooting methods:
|


