Snowflake - Lookup
Overview
SELECT [Output fields] FROM [Table name] WHERE
[C1 = V11 AND C2 = V21 AND...[Cn = Vn1] OR
[C1 = V12 AND C2 = V22 AND...[Cn = Vn2] OR
...................................... OR
[Cn = V1n AND Cm = V2m AND...[Cn = Vnm]aThe Snap ignores any duplicated lookup condition in the input document stream since it maintains a cache for lookup conditions internally.
Read-type Snap
-
Works in Ultra Tasks
Prerequisites
You must have minimum permissions on the database to execute Snowflake Snaps. To understand if you already have them, you must retrieve the current set of permissions. The following commands enable you to retrieve those permissions:
SHOW GRANTS ON DATABASE <database_name>
SHOW GRANTS ON SCHEMA <schema_name>
SHOW GRANTS TO USER <user_name>- Usage (DB and Schema): Privilege to use the database, role, and schema.
grant usage on database <database_name> to role <role_name>;
grant usage on schema <database_name>.<schema_name>;Learn more about Snowflake privileges: Access Control Privileges.
This Snap uses the LOOKUP command internally. It queries the database and retrieves a set of rows or defines the set of columns returned by a query.
Known Issues
Because of performance issues, all Snowflake Snaps now ignore the Cancel queued queries when pipeline is stopped or if it fails option for Manage Queued Queries, even when selected. Snaps behave as though the default Continue to execute queued queries when the Pipeline is stopped or if it fails option were selected.
Snap views
| View | Description | Examples of upstream and downstream Snaps |
|---|---|---|
| Input |
Each document should have values for one AND clause in the WHERE statement. Each document in the input view should contain a Map data of key-value entries. Input data may contain values needed to evaluate expressions in the Object type, Output fields, and Conditions properties. If the Pass-though on no lookup match property is unchecked, ensure input
data types match column data types in the database table. Otherwise, you may
encounter an error message |
|
| Output |
The output document includes the corresponding input data under the "original" key. If there are no results from the query, each output field will have a null value. Each document in the output view contains a Map data of key-value entries, where keys are the Output fields property values. The input data that has produced the corresponding output data is also included in the output data under the "original" key. |
|
| Error |
Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter when running the pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab. The available options are:
Learn more about Error handling in Pipelines. |
|
Snap settings
- Expression icon (
): Allows using JavaScript syntax to access SnapLogic Expressions to set field values dynamically (if enabled). If disabled, you can provide a static value. Learn more.
- SnapGPT (
): Generates SnapLogic Expressions based on natural language using SnapGPT. Learn more.
- Suggestion icon (
): Populates a list of values dynamically based on your Snap configuration. You can select only one attribute at a time using the icon. Type into the field if it supports a comma-separated list of values.
- Upload
 : Uploads files. Learn more.
: Uploads files. Learn more.
| Field / Field set | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
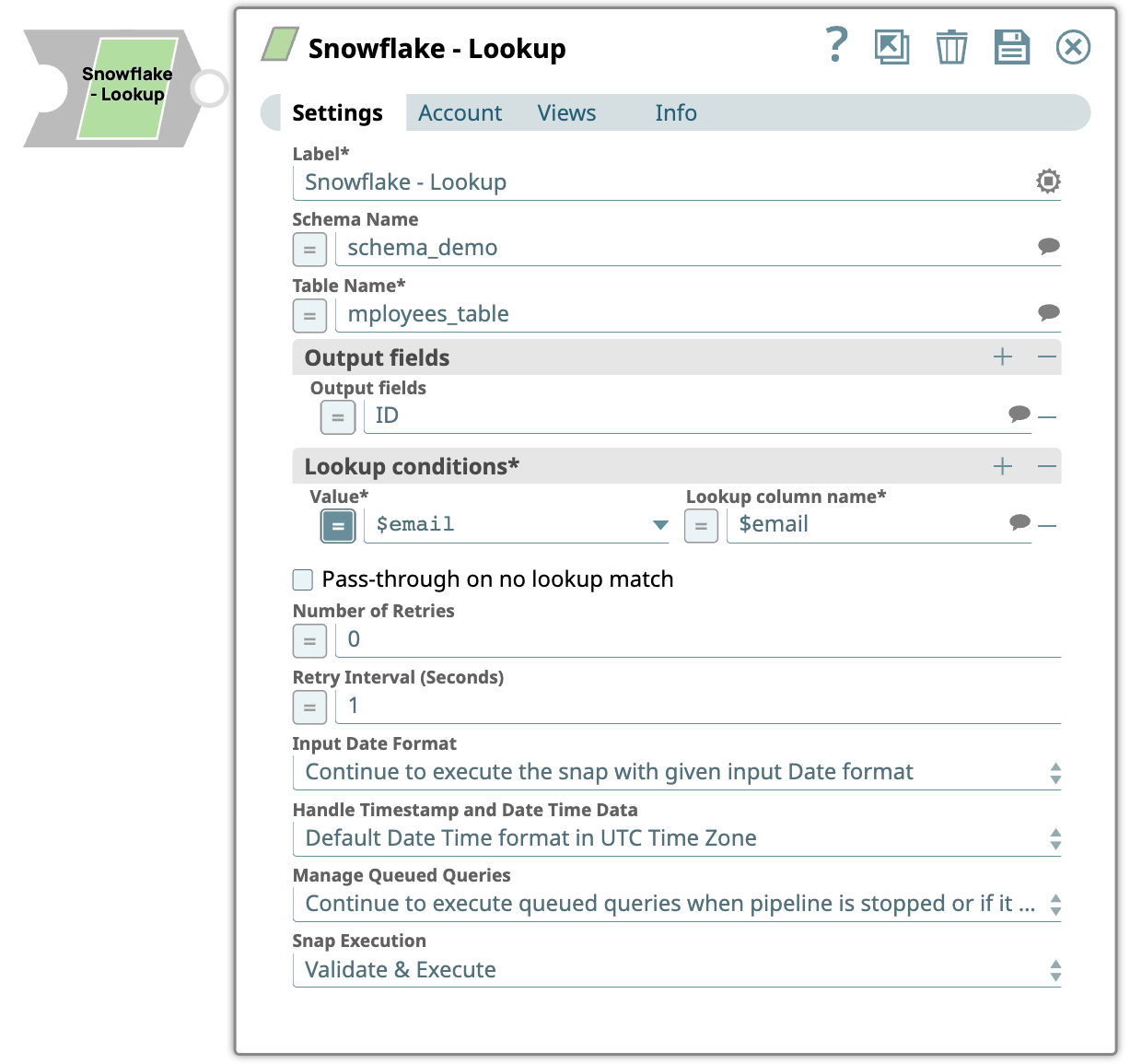
| Label | String | Required. Specify a unique name for the Snap. Modify this to be more appropriate, especially if there are more than one of the same Snap in the pipeline. |
| Schema Name | String/Expression | Required. Specify the database schema name. In case it
is not defined, then the suggestion for the Table Name retrieves all tables names of
all schemas. The property is suggestible and will retrieve available database
schemas during suggest values. Note: The values can be passed using the pipeline
parameters but not the upstream parameter. Default value: N/A Example: Schema_demo |
| Table Name | String/Expression | Required. Enter or select the name of the Snowflake SQL
table to execute the lookup query. Note:
Default value: N/A Example: employees_table |
| Output fields | String/Expression | Enter or select output field names for the Snowflake SQL SELECT
statement. Default value: N/A Example: ID |
| Lookup conditions | Use this field set to enter or select the lookup column name. | |
| Value | String/Expression | Enter or select the JSON path of the lookup column value. The value will be
provided by the input data field. Default value: N/A Example: $email |
| Lookup column name | String/Expression | Specify the lookup conditions are created by using the lookup column name and the lookup column value. Each row will build a condition, such aslookupColumn1 = $inputField. Each additional row will be concatenated using a logical AND. All rows together build the lookup condition being used to look up records in the lookup table. Default value: N/A Example: $email |
| Pass-through on no lookup match | Checkbox | Required. When there is no lookup matching an input
document, the input document will pass through to the output view if this property
is checked. Otherwise, it will be written to the error view as an error
condition. Default status: deselected |
| Number of retries | Integer/Expression | Specify the maximum number of retry attempts when the Snap fails to
read. Minimum Value: 0 Default value: 0 Example: 3 |
| Retry interval (seconds) | Integer/Expression | Specifies the minimum number of seconds the Snap must wait before each retry
attempt. Minimum Value: 1 Default value: 1 Example: 3 |
| Input Date Format | Dropdown list | The property has the following two options:
Default value: Continue to execute the snap with given input Date format Example: Auto Convert the format to Snowflake default format |
| Handle Timestamp and Date Time Data | Dropdown list | Choose an option for handling timestamp and date time data. The available
options are:
Note:
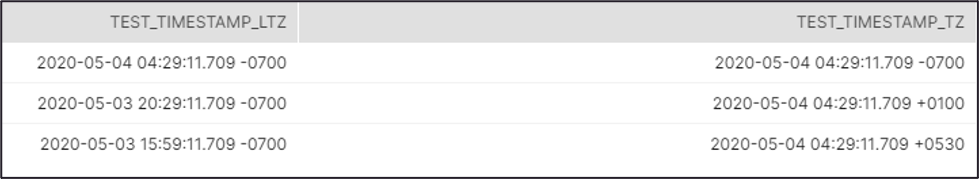
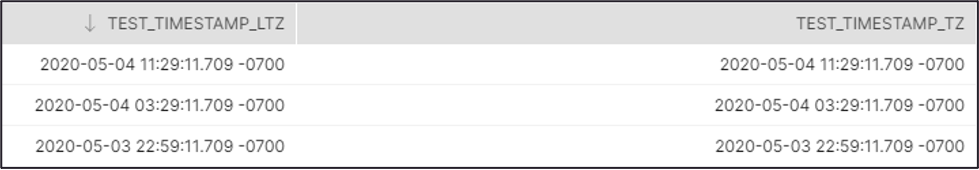
Recommendation: If you use the Timestamp TZ and Timestamp LTZ
in this Snap, we recommend you to use SnapLogic Date Time format in Regional
TimeZone to ensure that you get the Timestamp data output of the target
table in the same format as in the source table. Source Table Target Table |
| Manage Queued Queries | Dropdown list |
Default value: Select an option to determine whether the
Snap should continue or cancel the execution of the queued Snowflake Execute SQL
queries when you stop the pipeline.
Note: If you select Cancel queued queries when
the pipeline is stopped or if it fails, then the read queries under execution
are canceled, whereas the write type of queries under execution are not
canceled. Snowflake internally determines which queries are safe to be canceled
and cancels those queries. Default value: Continue to execute queued queries when the Pipeline is stopped or if it fails Example: Cancel queued queries when the pipeline is stopped or if it fails |
| Snap execution | Dropdown list |
Choose one of the three modes in
which the Snap executes. Available options are:
Default value: Execute only Example: Validate & Execute |