Snowflake - Execute
Overview
Write-type Snap
-
Works in Ultra Tasks
Prerequisites
You must have minimum permissions on the database to execute Snowflake Snaps. To understand if you already have them, you must retrieve the current set of permissions. The following commands enable you to retrieve those permissions:
SHOW GRANTS ON DATABASE <database_name>
SHOW GRANTS ON SCHEMA <schema_name>
SHOW GRANTS TO USER <user_name>- Usage (DB and Schema): Privilege to use the database, role, and schema.
- Create table: Privilege to create a table on the database. role, and schema.
grant usage on database <database_name> to role <role_name>;
grant usage on schema <database_name>.<schema_name>;
grant "CREATE TABLE" on database <database_name> to role <role_name>;
grant "CREATE TABLE" on schema <database_name>.<schema_name>;Learn more about Snowflake privileges: Access Control Privileges.
The permissions to grant for usage on database and creating tables depend on the queries you provide in this Snap.
Limitations
-
User-defined functions (UDFs) created in the Snowflake console can be executed using Snowflake - Execute Snap. See Execute-Snowflake Execute Snap supports UDFs in examples.
- The Snap may break existing Pipelines if the JDBC Driver is updated to a newer version.
sNote: Snowflake Execute and Multi-Execute Snaps may break existing Pipelines if the JDBC Driver is updated to a newer version.
With the updated JDBC driver (version 3.12.3), the Snowflake Execute and Multi-Execute Snaps' output displays a Status of "-1" instead of "0" without the Message field upon successfully executing DDL statements. If your Pipelines use these Snaps and downstream Snaps use the Status field's value from these, you must modify the downstream Snaps to proceed on a status value of -1 instead of 0.
This change in the Snap behavior follows from the change introduced in the Snowflake JDBC driver in version 3.8.1:
"Statement.getUpdateCount() and PreparedStatement.getUpdateCount() return the number of rows updated by DML statements. For all other types of statements, including queries, they return -1."
Known Issues
Because of performance issues, all Snowflake Snaps now ignore the Cancel queued queries when pipeline is stopped or if it fails option for Manage Queued Queries, even when selected. Snaps behave as though the default Continue to execute queued queries when the Pipeline is stopped or if it fails option were selected.
Behavior change
- In 4.26, when the stored procedures were called using the Database Execute Snaps, the queries were treated as write queries instead of read queries. So the output displayed message and status keys after executing the stored procedure.
- In 4.27, all the Database Execute Snaps run stored procedures correctly, that is, the queries are treated as read queries. The output now displays message key, and OUT params of the procedure (if any). The status key is not displayed.
- If the stored procedure has no OUT parameters, only the message key is displayed with value success.
- From 4.30 Release, the Snowflake Execute Snap writes the output value as-is for FLOAT or DOUBLE datatype columns if these columns have the value as NaN (Not a Number). Earlier, the Snap displayed an exception error when the FLOAT or DOUBLE datatype column has the value as NaN. This behavior is not backward compatible.
Snap views
| View | Description | Examples of upstream and downstream Snaps |
|---|---|---|
| Input | The SQL statement to execute. If the Where clause is defined, then the clause substitutes incoming values for a given expression. | |
| Output | If an output view is available and an update/insert/merge/delete statement was executed, then the original document that was used to create the statement will be output with the status of the executed statement. | |
| Error |
Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter when running the pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab. The available options are:
Learn more about Error handling in Pipelines. |
|
Snap settings
- Expression icon (
): Allows using JavaScript syntax to access SnapLogic Expressions to set field values dynamically (if enabled). If disabled, you can provide a static value. Learn more.
- SnapGPT (
): Generates SnapLogic Expressions based on natural language using SnapGPT. Learn more.
- Suggestion icon (
): Populates a list of values dynamically based on your Snap configuration. You can select only one attribute at a time using the icon. Type into the field if it supports a comma-separated list of values.
- Upload
 : Uploads files. Learn more.
: Uploads files. Learn more.
| Field / Field set | Type | Description | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label | String | Required. Specify a unique name for the Snap. Modify this to be more appropriate, especially if there are more than one of the same Snap in the pipeline. | |||||||||
| SQL Statement | String/Expression | Required. Specify the Snowflake SQL statement to execute
on the server. Note: We recommend you to add a single query in the SQL Statement
field. Document value substitution is performed on literals starting with '$', for example, $people.name is substituted with its value available in the incoming document. In DB Execute Snaps, if the Snowflake SQL statement is not an expression, the JSON path, such as $para, is allowed in the WHERE clause only. If the query statement starts with SELECT (case-insensitive), the Snap regards it as a select-type query and executes once per input document. If not, the Snap regards it as a write-type query and executes in batch mode. This Snap does not allow you to inject Snowflake SQL, for example, select * from people where $columnName = abc. Only values can be substituted since it uses prepared statements for execution, which, for example, results in select * from people where address = ?. Without using expressions
Note: Using expressions that join strings together to create SQL queries or
conditions has a potential SQL injection risk and is hence unsafe. Ensure that you
understand all implications and risks involved before using concatenation of
strings with '=' Expression enabled. Note:
Note: Single quotes in values must be escaped Any relational
database (RDBMS) treats single quotes (
Default value: N/A Example: INSERT into SnapLogic.book (id, book) VALUES ($id,$book) |
|||||||||
| Query type | Dropdown list/Expression | Select the type of query for your SQL statement (Read or Write). When
Auto is selected, the Snap tries to determine the query
type automatically. If the execution result of the query is not as expected, you can
change the query type to Read or Write. Default value: Auto Example: Read |
|||||||||
| Pass through | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to enable the Snap to pass the input document to the
output view under the key named original. This option applies only
to the Execute Snaps with SELECT statement. Default status: Selected |
|||||||||
| Ignore empty result | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to not write any document to the output view when a SELECT
operation does not produce any result. If this checkbox is not selected and the
Pass-through checkbox is selected, the input document is passed through to the
output view. Default status: Deselected |
|||||||||
| Number of Retries | Integer | Specify the maximum number of attempts to be made to receive a response. The
request is terminated if the attempts do not result in a response.
Minimum Value: 0 Note: Ensure that the local drive has sufficient free
disk space to store the temporary local file. Default value: 0 Example: 3 |
|||||||||
| Retry interval (seconds) | Integer | Specify the time interval between two successive retry requests. A retry
happens only when the previous attempt resulted in an exception. Default value: 1 Example: 10 |
|||||||||
| Use Result Query | Checkbox |
Select this checkbox to write the query execution result to the Snap's output
view after the successful execution. The output of the Snap will be enclosed
within the key This option allows users to effectively track the query's execution by clearly indicating the successful execution and the number of records affected, if any, after the execution. Default status: deselected |
|||||||||
| Handle Timestamp and Date Time Data | Dropdown list | Choose an option for handling timestamp and date time data. The available
options are:
Note:
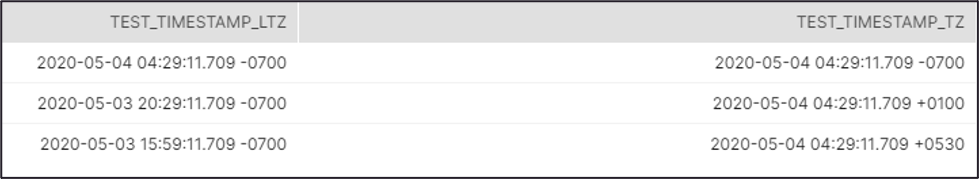
Recommendation: If you use the Timestamp TZ and Timestamp LTZ in this Snap,
we recommend you to use SnapLogic Date Time format in Regional TimeZone to
ensure that you get the Timestamp data output of the target table in the same
format as in the source table. Source Table Target Table 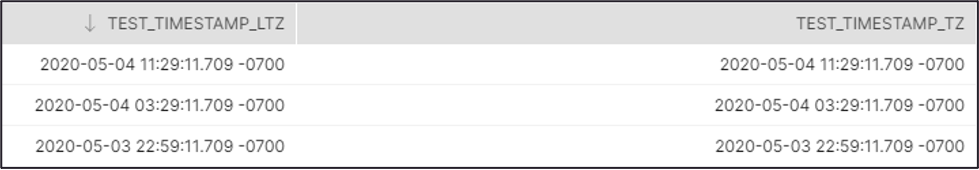 |
|||||||||
| Manage Queued Queries | Dropdown list | Select an option from the list to determine whether the Snap should continue
or cancel the execution of the queued Snowflake Execute SQL queries when you stop
the pipeline. The available options are:
Note: If you select Cancel queued queries when the pipeline is stopped or if it
fails, then the read queries under execution are canceled, whereas the write
type of queries under execution are not canceled. Snowflake internally
determines which queries are safe to be canceled and cancels those
queries.
Default value: Continue to execute queued queries when the Pipeline is stopped or if it fails Example: Cancel queued queries when the pipeline is stopped or if it fails |
|||||||||
| Snap execution | Dropdown list | Choose one of the three modes in which the Snap executes. Available options
are:
|